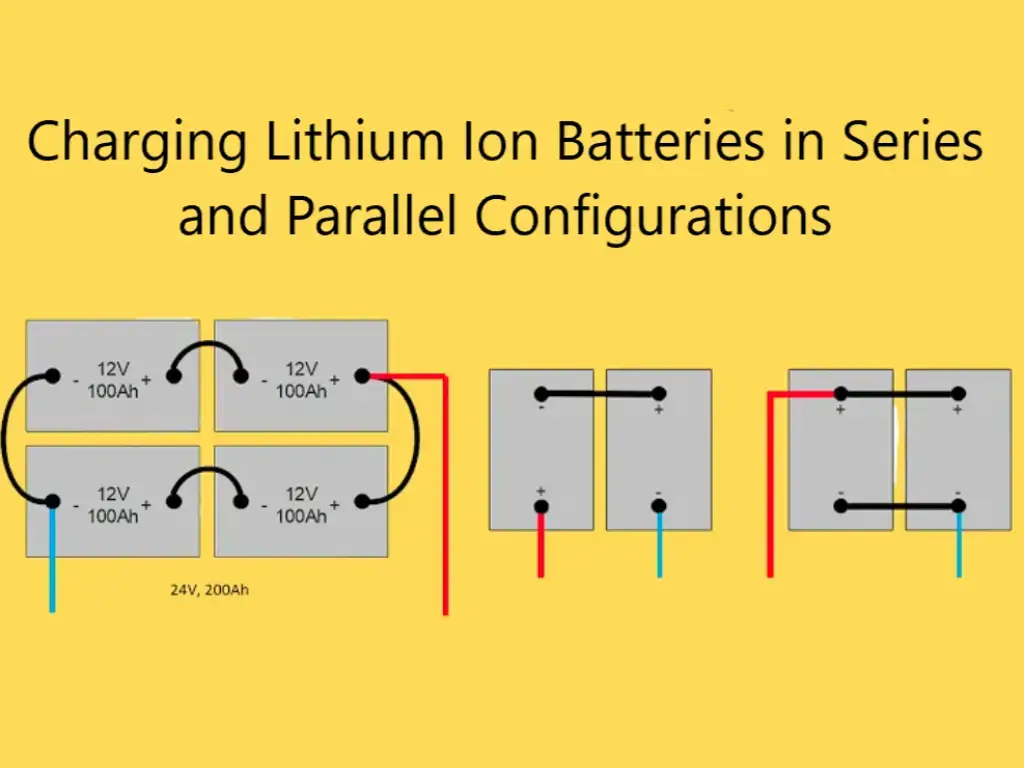
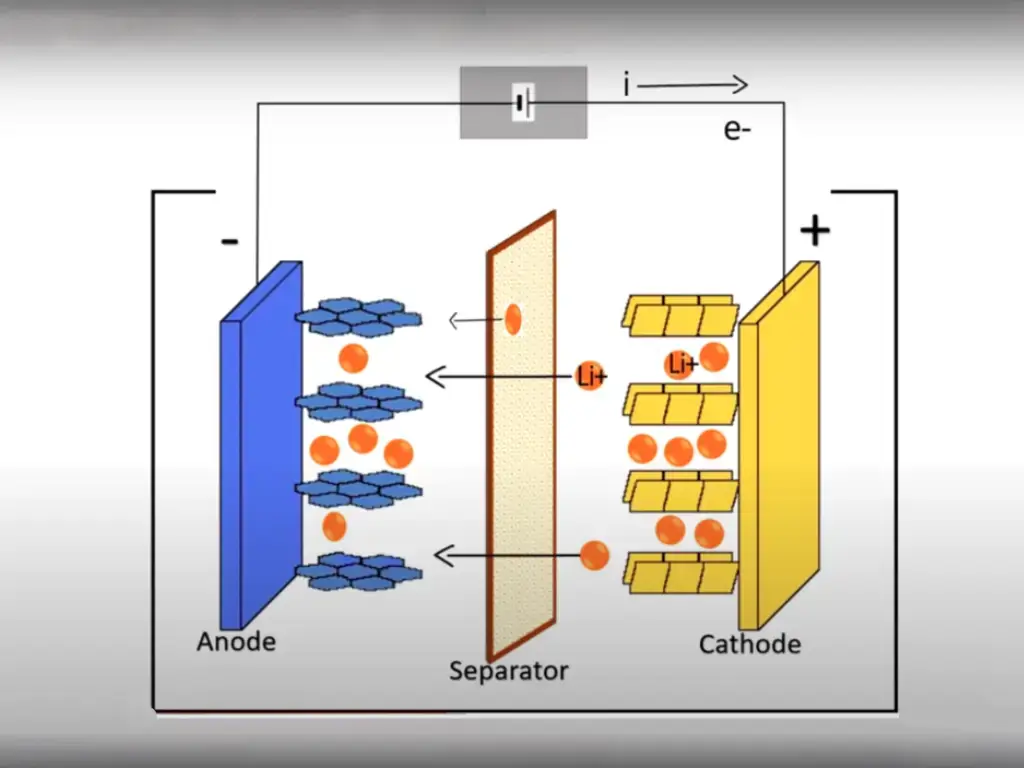
A deep cycle battery refers to a battery with a dod higher than 80%, and does not damage the battery life; lead-acid batteries cannot be deeply discharged frequently, otherwise the battery itself will be greatly damaged.

Deep cycle battery types
At present, the deep cycle batteries are: lithium titanate batteries, lithium iron phosphate batteries, and ternary lithium batteries. Although the lithium titanate battery has a long life, its high cost and large volume make it not widely used. The most widely used deep cycle batteries are ternary lithium batteries and lithium iron phosphate batteries.
What is a lithium iron phosphate battery?
A lithium iron phosphate battery is a type of lithium ion battery, which refers to a lithium ion battery using lithium iron phosphate as a positive electrode material. It is characterized by strong safety and stability, high temperature resistance and good cycle performance.
How long is the real life of a lithium iron phosphate battery pack?
The cycle life of long-life lead-acid batteries is about 300 times, and the maximum is 500 times. The lithium iron phosphate power battery has a cycle life of more than 2000 times. The lead-acid battery of the same quality is “new half year, old half year, and maintenance and maintenance for half a year”, which is 1~1.5 years at most, and the lithium iron phosphate battery pack is used under the same conditions, and the theoretical life will reach 7~8 years. However, due to the poor low temperature performance of lithium iron phosphate batteries, the life of lithium iron phosphate batteries will be relatively short in areas with low temperatures.
Which is the longer real life of ternary lithium and lithium iron phosphate?
The ternary lithium battery material battery is cycled 3900 times, the remaining capacity is 66%, and the lithium iron phosphate battery pack is cycled 5000 times, the remaining capacity is 84%, and the cycle life is more obvious than the ternary material battery and the lithium iron phosphate battery. According to the remaining capacity/initial capacity=80% as the end point of the test, the current 1C cycle life of the ternary material battery laboratory is about 2500 times, the 1C cycle life of the lithium iron phosphate battery laboratory is more than 3500 times, and some of them are more than 5000 times. Therefore, the actual service life of lithium iron phosphate batteries is longer than that of ternary lithium batteries.
The lithium iron phosphate battery pack has stable output voltage, high output voltage, stable performance, large capacity, long service life, wide operating temperature range, good safety, and environmental protection and no pollution. Therefore, there is a lot of room for improvement in the future development of lithium batteries. .
The advantages of lithium iron phosphate battery pack compared with lead-acid battery
1. Large capacity. The lithium battery cell can be made into 5Ah~1000Ah (1Ah=1000mAh), while the lead-acid battery 2V cell is usually 100Ah~150Ah, and the variation range is small.
2. Light weight. The volume of the lithium iron phosphate battery pack of the same capacity is 2/3 of the volume of the lead-acid battery, and the weight is 1/3 of the latter.
3. Strong fast charging capability. The starting current of lithium iron phosphate battery pack can reach 2C, which can realize high-rate charging; the current requirement of lead-acid battery is generally between 0.1C and 0.2C, which cannot achieve fast charging performance.
4. Environmental protection. Lead-acid batteries contain a large amount of heavy metals – lead, which produces waste liquid, while lithium iron phosphate battery packs do not contain any heavy metals and are pollution-free during production and use.
5. Cost-effective. Although lead-acid batteries are cheaper than lithium iron phosphate batteries because of their cheap materials, the purchase cost is lower than that of lithium iron phosphate batteries, but they are less economical than lithium iron phosphate batteries in terms of service life and routine maintenance. The practical application results show that the cost performance of lithium iron phosphate batteries is more than 4 times that of lead-acid batteries.
The lithium iron phosphate power battery is charged and discharged at 1C at room temperature. The capacity of the monomer is still greater than 80% after 2000 cycles, and the 3C cycle life reaches more than 800 times. The life is relatively long among all batteries.
What is the real cycle of lithium iron phosphate batteries for different purposes?
At present, the lithium iron phosphate batteries on the market are marked with a cycle life of about 2000 times. This refers to the ideal number of stable normal low current charge and discharge and application in normal temperature environment, but in fact, under different usage conditions, the real life cycle of lithium iron phosphate batteries The numbers are different.
Lithium iron phosphate battery is used in normal temperature environment
(1) Small current charge and discharge
The use in this case is basically used in 3C electronic products, and the cycle life is more than 2000 times;
(2) High rate stable charge and discharge use
Most of the applications of high-rate discharge are power-type lithium batteries, and most of them are used in applications that provide power to motors, such as new energy vehicles, electric vehicles, and fishing boat electromechanical power supplies. Because most lithium iron phosphate batteries operate under high load conditions, the decay time of battery materials is accelerated, and the cycle life is drastically reduced. Poor quality batteries may only have about 500 cycles; strong battery brand manufacturers, in The equipment technology and material application will be better, and the quality of the battery will be better, but the cycle life will be about 800 times.
(3) High rate unstable charge and discharge use
The lithium iron phosphate battery used in this case will have a shorter lifespan, and it will be scrapped about 300 times. Unstable discharge of the battery, high and low, will have a greater effect on battery attenuation.
Lithium iron phosphate battery used in high temperature environment
The high-temperature performance of lithium iron phosphate batteries is not very mature at present. The operating temperature is -20°C to 125°C. This temperature range is the theoretical value, and the actual application temperature range is smaller.
(1) Small current charge and discharge
The application of lithium iron phosphate batteries in this field basically has a cycle life of more than 1000 times; because it is used at high temperatures, the damage to the battery is relatively large.
(2) High rate stable charge and discharge use
Most of the applications of high-rate discharge of batteries in high temperature environments are power-type lithium batteries, and most of them are used to provide power to motors. The cells produced by domestic powerful lithium battery manufacturers are mostly used in new energy vehicles and electric vehicles. , fishing boat electromechanical power supply, etc., battery manufacturers with poor strength are mostly used in some relatively small fields, such as medical treatment, boiler equipment startup, etc.
Because most lithium iron phosphate batteries operate under high load conditions, the decay time of battery materials is accelerated, and the cycle life is drastically reduced, and the cycle life is about 500 times.
(3) High rate unstable charge and discharge use
In a high temperature environment, the discharge rate is unstable and the lithium iron phosphate battery is used, which will cause greater damage to the battery and a relatively low cycle life. Tests on the cells of several battery manufacturers have found that 250 to 300 times, the battery cycle is used up.
Lithium iron phosphate battery used in low temperature environment
The low temperature environment has a greater impact on the performance of the lithium iron phosphate battery than the high temperature. The lithium iron phosphate battery works below -20 °C to -40 °C, and the life is significantly reduced. The discharge current range is 0.2C to 1C, and the discharge capacity is 50%. -60%, the lower the temperature, the worse the discharge capacity. There are not many low-temperature lithium iron phosphate batteries used in mature applications, with a temperature range of -20°C to 55°C and a cycle life of about 300 times.
The experiment of putting lithium iron phosphate battery to zero voltage
Putting the lithium iron phosphate battery into the zero-voltage experiment, you will find that after the battery is fully charged in 3 days, it will continue to discharge in such an environment, and it will be found that its capacity will change very little. It means that its capacity recovery is very good.
Finally, the production of lithium iron phosphate batteries is subject to patent disputes in foreign countries, which is one of the reasons why ternary cathode materials lithium-ion batteries are widely used in foreign electric vehicles.
Keheng Self-Heating Battery
100AH 12V Low Temperature Heating Enable
Keheng New Energy’s Range Of Products
DEEP CYCLE BATTERIES With BMS(lifepo4 Lithium Battery)
Low Temperature 24V 60AH Deep Cycle LiFePO4 Battery