What is thermal runaway?
Thermal runaway is a process that is accelerated by an increase in temperature, thereby releasing energy for further higher temperatures, which often leads to various destructive consequences if not addressed in time.
This phenomenon occurs in several areas. Nuclear fusion reactions caused by runaway stars in astrophysics lead to nova and several types of supernova explosions. In civil engineering, thermal runaway also occurs when the heat released by a large amount of cured concrete is uncontrolled.
But these types of thermal runaways are still a minority, and more thermal runaways occur in the fields of chemistry and electrical engineering. The strong exothermic reaction is accelerated due to the increase of temperature, and most of its applications occur in the use of batteries, which are often accompanied by explosions and fires.
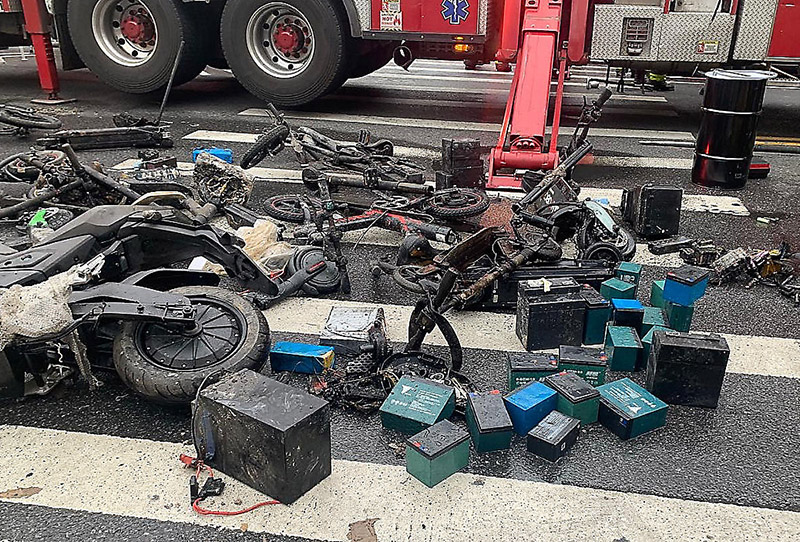

What is battery thermal runaway?
When the battery is due to some failure or improper handling, the battery starts to cause various chain reactions uncontrollably. At this time, the internal temperature of the battery has exceeded the maximum temperature that the battery can withstand, and it often emits a lot of heat. In a worse situation, it may explode or cause a fire.It occurs more frequently in lithium-ion batteries, especially in electric vehicles and mobile phone applications.
In thermal runaway, the temperature of the battery rises rapidly (in milliseconds), and the chain reaction of stored battery energy creates extremely high temperatures (about 752 degrees Fahrenheit / 400 degrees Celsius – the temperature of a typical fire room).
process
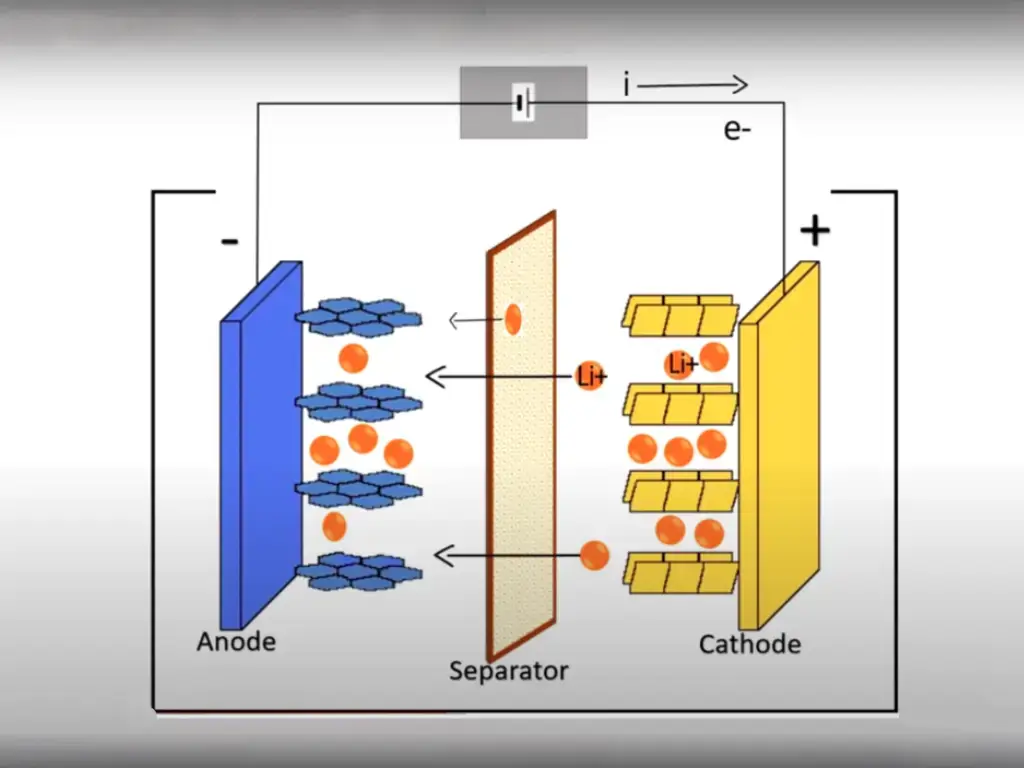
The thermal runaway of the battery often starts from the decomposition of the negative electrode SEI film in the battery cell, and then the separator is decomposed and melted, causing the negative electrode to react with the electrolyte, and then the positive electrode and the electrolyte will be decomposed, resulting in large-scale internal short circuit, resulting in electrolysis. The liquid burned, and then spread to other cells, causing severe thermal runaway, causing the entire battery pack to spontaneously ignite.
(SEI film: The SEI film is formed during the first charging of the lithium battery. A passivation film formed by the reaction between the negative electrode material and the electrolyte, its function is to coat the negative electrode material on the one hand and protect its structure from damage; on the other hand, It allows lithium ions to pass through and intercalate into the negative electrode material.)
Causes and suggestions for battery thermal runaway
overcharge
The battery is overcharged beyond its maximum safe voltage, which not only damages the battery itself, but can also trigger a fire in severe cases. A similar incident occurred in China in 2022. The reason was that the overcharge of the pure electric bus triggered the thermal runaway of the battery, and the battery management system itself lacked the safety function of the overcharge circuit.
Method suggestion: Find the fault of the charger, which can be solved by the full redundancy of the charger. Secondly, it is necessary to observe whether the battery management system carried by its own battery complies with the regulations, for example, whether the voltage of each battery can be monitored.
Temperature is too high
Excessive temperature is also a cause of thermal runaway in the battery. Due to the unreasonable selection and thermal design of the battery, the internal short circuit of the battery is caused, and it is also necessary to avoid the short circuit of the battery caused by external misoperation.
In consideration of battery design materials, materials to prevent thermal runaway or to block the reaction of this phenomenon have been developed.From the perspective of battery management, it realizes temperature safety warning and realizes battery danger warning.
In the past few years, “non-firing batteries” have become a new trend in China. In the industry, there has been a “big discussion about who is safer between iron-lithium and ternary”. It was first initiated by companies such as CATL, BYD, and
SVOLT. At the same time, Chinese car companies started the road to “no fire, no smoke, no explosion”. At present, Keheng is the application of “never fire” lithium iron phosphate batteries.
Internal short circuit
In 2006, a Boeing 787 caught fire after a battery exploded. The cause may originate from the internal short circuit caused by the presence of metal objects in the electrodes and separators, but experts cannot accurately confirm whether it is the cause.
To solve this problem, it is best to find a battery manufacturer with good product quality. The selected battery management system (BMS) is compliant and capable of timely detection of batteries with internal short circuits.
caused by external collision
A crash is a typical way to trigger a thermal runaway. In response to multiple Tesla car fires in China, Tsinghua University and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology jointly conducted an analysis of Tesla’s crashes in the United States.
In addition to the correct operation of the operator, the solution to this method also requires the battery to be designed for safety protection, which may require the R&D personnel to better understand the reason for the process.
conclusion
At present, BMS monitoring on the market has matured, including monitoring and management of battery voltage, battery current, battery temperature, battery charge balance, charge control, and internal short-circuit detection. The realization of battery thermal runaway management detection from materials to safety design has slowly driven the healthy development of the entire battery industry.
If you are using a lead acid battery, when the battery has an internal short circuit, enough heat is generated to cause the internal acid to boil, and all you may smell is rotten eggs – sulfur. While this won’t start a fire, the danger of spilling battery acid is far greater than any fire or explosion. (So I suggest that if you buy lead-acid batteries, try to choose an excellent manufacturer)