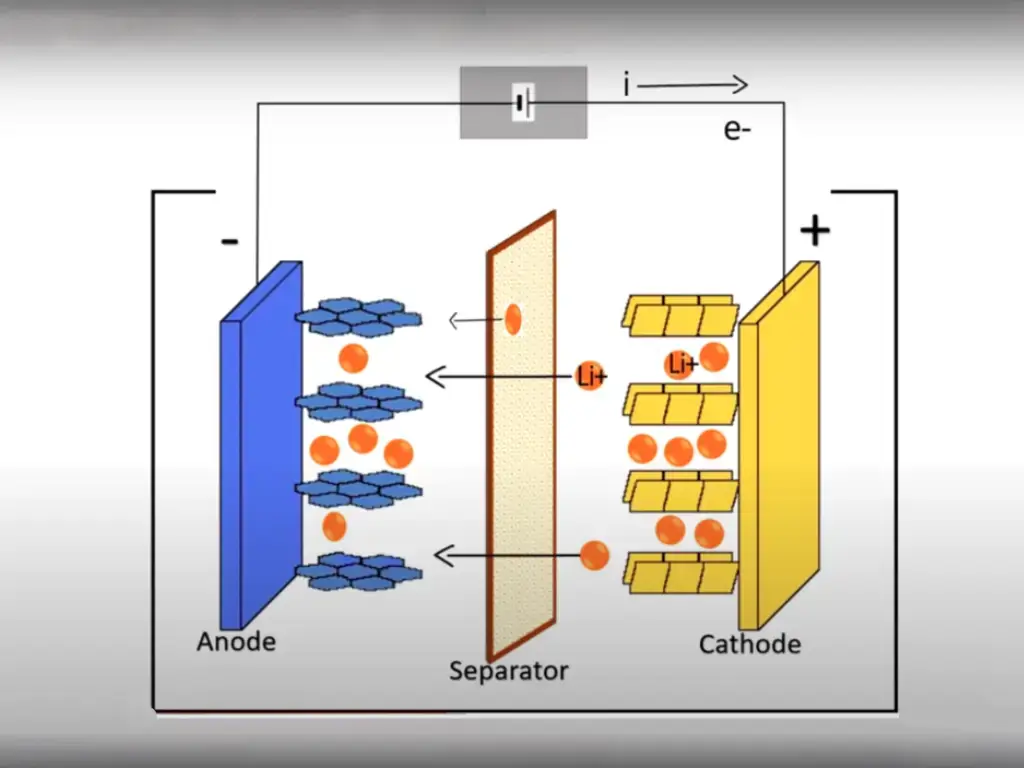
All lithium battery protection solutions take the lithium battery BMS protection board as the carrier and the protection circuit as the manifestation. The protection circuit is usually composed of a protection IC and two power MOSFETs. The protection IC is responsible for monitoring relevant parameters, and the MOSFET is responsible for implementing power protection.
In the design of lithium battery protection scheme, the following six purposes must be achieved:
- High precision of overcharge protection: the safety is taken into account when the battery is fully charged. The current accuracy is 25mV, which needs to be further improved;
- Reduce the power consumption of the protection IC: when the MOSFET is turned off, the battery itself still has self-discharge and the current consumption of the protection IC. It is necessary to minimize the current consumption of the protection IC as much as possible;
- Over-current/short-circuit protection requires low detection voltage and high precision. During overcurrent/short circuit, the Rds(on) of the MOSFET is used as the inductive impedance to monitor the voltage drop process. If the voltage at this time is higher than the current detection voltage, the discharge will stop. Therefore, the impedance value should be kept as low as possible. About 20mΩ~30mΩ;
- High voltage resistance: when charging, there will be a high voltage momentarily when the battery pack is connected to the charger;
- Low battery power consumption: The lithium battery current in the protection state must be less than 0.1μA;
- Zero volt rechargeable: Some batteries have been discharged for too long or other abnormal reasons, causing the voltage to drop to zero volts, so the protection IC needs to be rechargeable at zero volts.