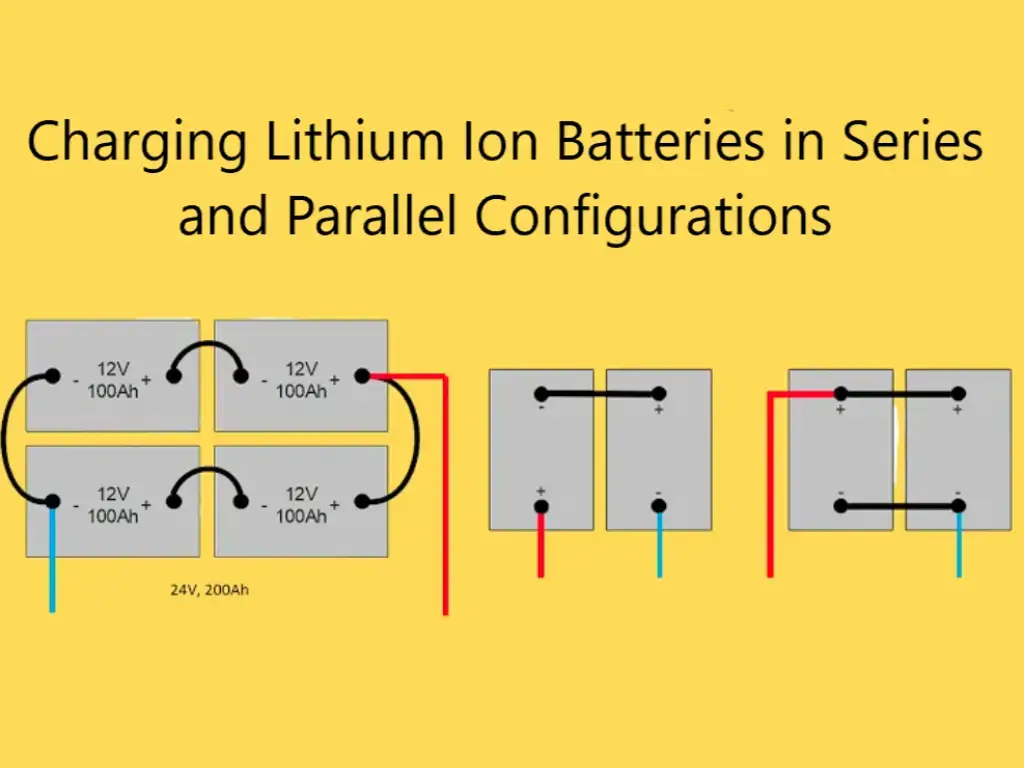
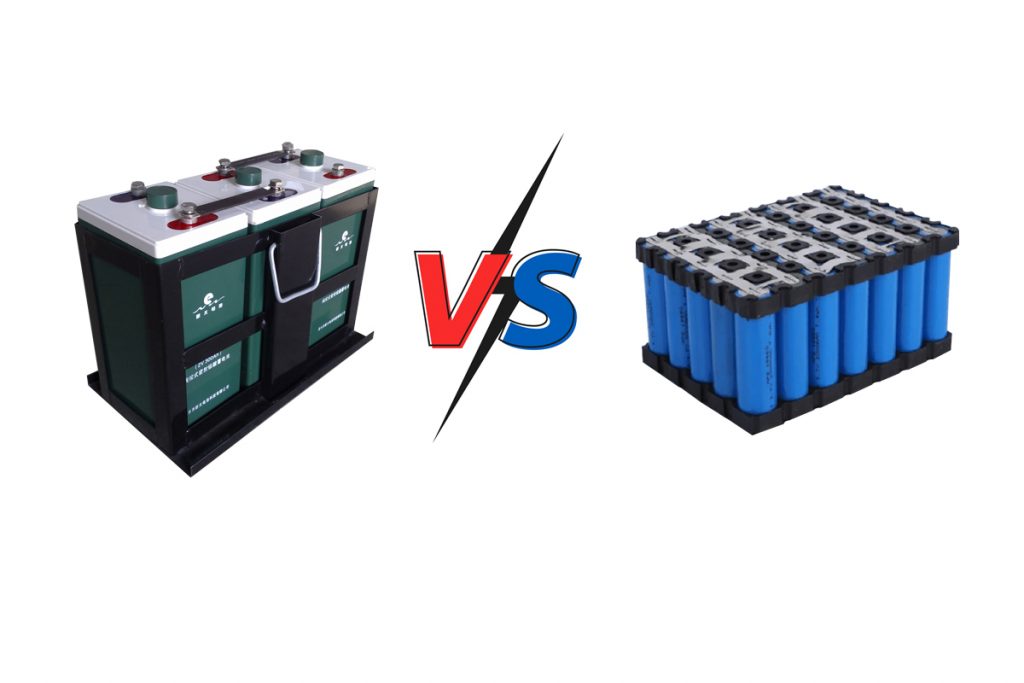
On board or on your RV, batteries play a crucial role. AGM battery, lithium battery… Historical technology, sealed lead batteries are gradually giving way to more modern technologies. But not all of them are equal, depending on the desired applications and the budget. Discover the advantages and disadvantages of lithium battery VS AGM battery.

LiFePO4 battery overview
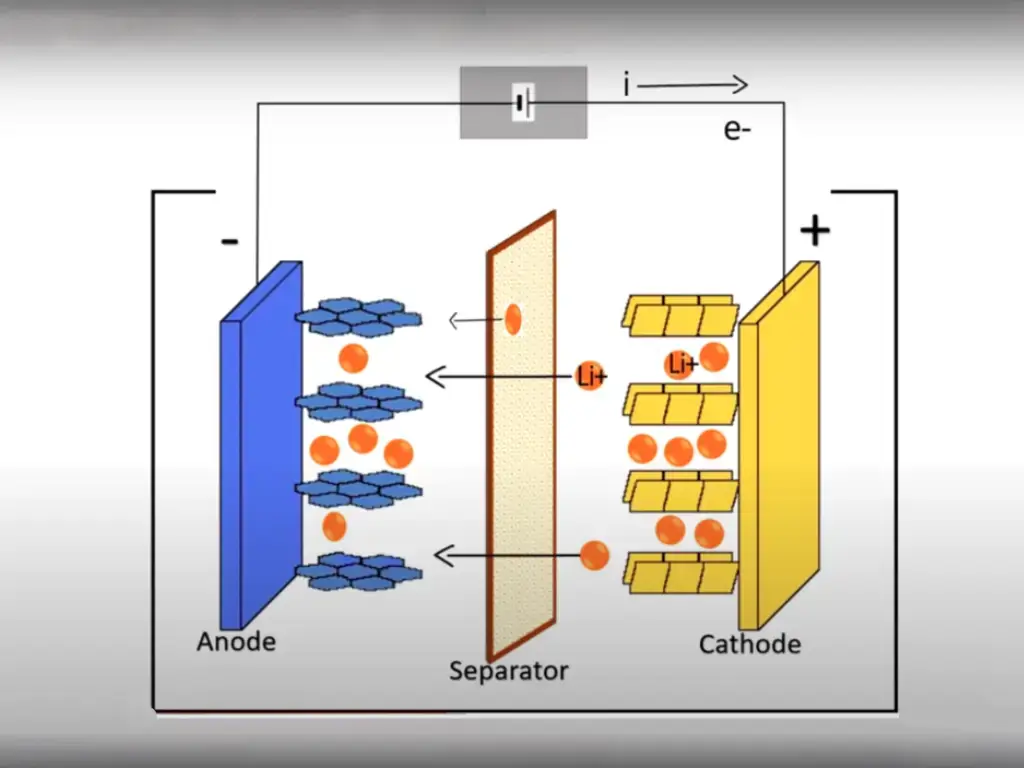
Lithium Iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries are a type of lithium ion (Li-Ion) rechargeable battery. Their benefits over the more traditional cobalt-based Li-Ion batteries are increased power output, faster charging, reduced weight and longer lifetime. The batteries also have better safety characteristics and do not explode under extreme conditions. LiFePO4 batteries also eliminate the concerns of cobolt entering the environment through improper disposal once they have expired.
AGM battery overview
AGM stands for “Absorbed Glass Mat”. As the name suggests, AGM batteries have a gel electrolyte and a glass fiber separator between the plates. A hybrid version of the lead-acid and gel batteries, AGM batteries have become increasingly popular in the marine sector over the last 10 years. They offer an excellent compromise between these two technologies: more efficient than lead-acid batteries and less expensive than gel batteries. For the same weight, an AGM battery offers almost twice the power of a lead-acid battery (18kg for 800A). They also have a longer life (self-discharge rate between 1 and 3% per month). On average, AGM batteries are 30% more expensive than lead-acid batteries, but they are relatively easy to find on the market. On the other hand, it should be noted that some models do not support total discharge. It is thus advised not to exceed 80% of discharge, in order not to damage it. Price: 330 euros for 150Ah
Lithium Battery VS AGM Battery(The Comparison Between Both)
1.Lifespan and cost
Budgets play a huge role in deciding which battery to get. With Lithium batteries being more expensive to begin with, it can seem like a no-brainer to go with an AGM. But what causes this difference? AGM batteries remain less expensive because the materials used to make them are inexpensive and widely available. Lithium batteries, on the other hand, use more expensive materials with some being harder to come by (i.e. lithium).
Another part of the decision-making process to consider is the lifespan of these batteries. This is where the initial cost of the Lithium could be offset. The following points highlight the differences between lithium and AGM:
- AGM batteries are sensitive to depth of discharge. This means the deeper the battery is discharged, the fewer cycles it has.
- AGM batteries are generally recommended to only be discharged to 50% of their capacity to maximize their cycle life. This limited depth of discharge (DOD) of 50% means that more batteries are required to achieve the desired capacity. This means more upfront costs, and more space needed to store them.
- A lithium (LiFePO4) battery, on the other hand, is not affected much by depth of discharge so it boasts a much longer cycle life. Its DOD of 80-90% means fewer batteries are required to achieve the desired capacity. Fewer batteries mean less space needed to store them.
More on discharge depths later.
Initial Cost Per Capacity ($/kWh):
AGM – 221; Lithium – 530
Initial Cost Per Life Cycle ($/kWh):
AGM – 0.71; Lithium – 0.19
2.Depth of Discharge
This refers to the percentage of a battery that can be discharged without inflicting damage. Lithium-ion can generally discharge around 86-98% while lead-acid can handle closer to 30-50% discharge. This means at any given moment, a lithium-ion battery has over a 30% larger operating range. It also means lithium-ion batteries are less prone to the damage that comes from exceeding the depth of discharge.
3.Useable energy
As stated earlier most batteries Ah rating are quoted at the 20 hr rate. In the image below for the lead acid battery, if that were a 100 Ah battery at the 20 hr rate, you can see that 0.05C means 100 x 0.05 = 5 Amps for 20 hours = 100 Ah available until the battery is totally flat. As we use only 50% of the battery we can see that the voltage will still be 24 V at 50% DOD for a 5 Amp load over 10 hours, and therefore we would have consumed 50 Ah.
Increasing the current draw (as the graphs below show) can affect the useable energy available and battery voltage. This effective shrinkage in the rating is known as Peukert’s effect. With lead acid the higher the load, the more you need to increase the Ah capacity of your battery to help alleviate this. With Lithium however a load of even 10 times greater at 0.5C can still have a terminal voltage of 24V at 80% DOD/20% SOC, without going up on the Ah rating of the battery. This is what makes Lithium particularly suitable for high loads.
4.Capacity
While not as crucial for stationary applications, it is important to note that the higher energy density of lithium-ion means that it can store more energy per mass than AGM. This means systems can be smaller and lighter while providing the same amount of output.
5.Weight
Most Ah ratings of batteries regardless of type are specified at the 20 hour rate. This was fine in the days of light loads, but as the number of loads and the size of loads has increased over time, we also need to look at high short term loads, medium and longer term ones for differing types of equipment. This can mean a large battery pack. At the extremes we might have air conditioning running for 10 hours using 10 kW, compared to an LED light using 100 Watts in that time. Balancing these differing requirements and all the loads inbetween becomes key. With a large pack as shown below to achieve this, it becomes clear just how heavy Lead Acid can be compared to Lithium. 1360/336 = 4 times heavier.
6.Warranty
A lithium-ion battery can typically be warrantied for up to 15 years, whereas other battery types generally are warrantied for only a maximum of 1 year.
In conclusion
Lithium batteries have some major upsides compared to all lead-acid batteries. They’re a favorite for their lower weight and higher energy efficiency, the ability to fully discharge them, better operation in extreme temperatures, and longer life overall.
The only application where an AGM battery will currently outperform lithium is in engine starting applications. They are good at providing huge amounts of current for short periods of time as long as they are recharged immediately.