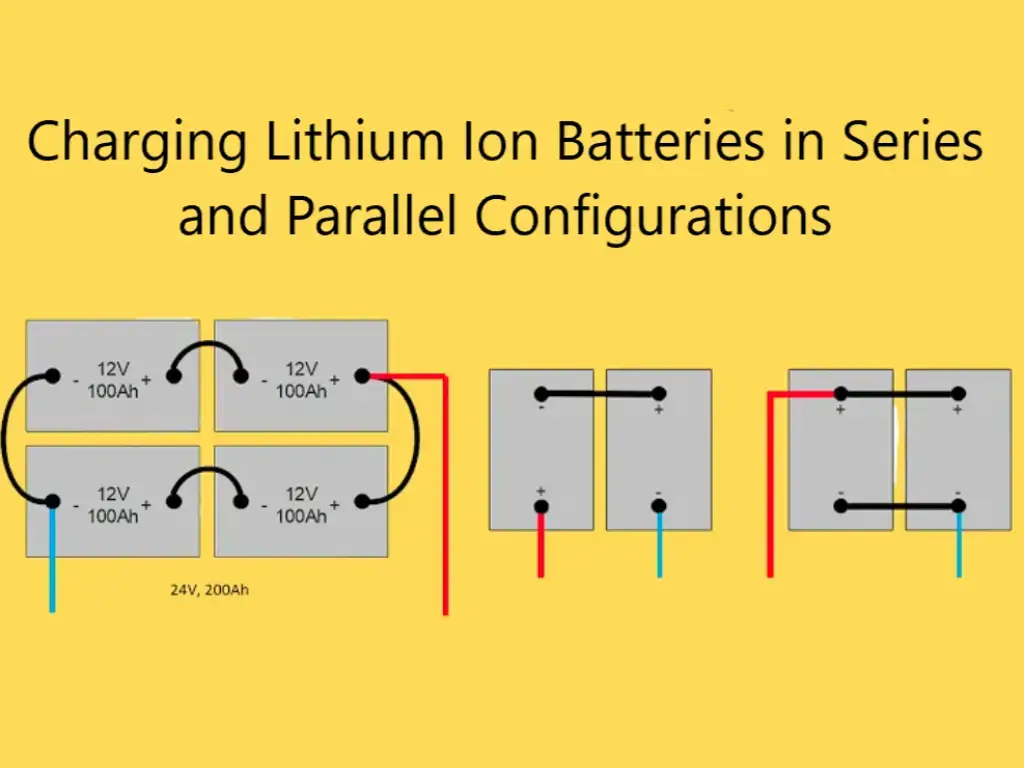
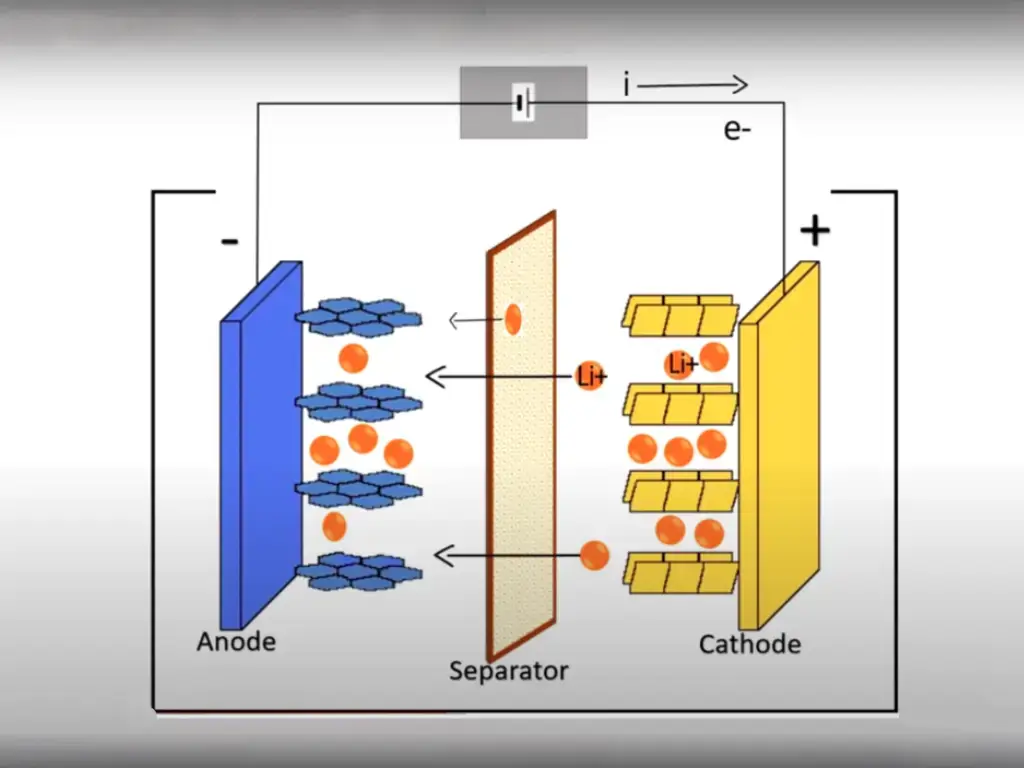
Many people are using lithium batteries now, but they don’t know what to do when they encounter problems during use. I will list some of these questions to answer them today.

Why does the battery have zero voltage (low voltage)? and how to deal with it?
1) Whether the battery is subject to external short circuit or over-discharge or reverse charging (reverse the positive and negative poles of the battery or the charger, it is equivalent to forced over-discharge when the battery is charging); whether the electrical circuit is normal; whether the spot welding product battery is There are burn marks.
2) Whether the battery is continuously overcharged by high rate and high current, which causes the battery movement to expand, and the internal positive and negative electrodes are directly contacted and short-circuited.
Approach:
1) Understand the specific usage of the user’s battery;
2) Charge the battery of the same type and connect it to the electrical appliance to determine whether the electrical appliance is normal;
3) Charge the battery with 1C current for 30 minutes, and leave it in the open circuit for about 10 minutes. If the open circuit voltage of the battery is stable within the normal voltage range of the battery, the battery can basically return to normal. If the battery has been damaged, the voltage cannot be recovered; if the battery is not in use and this phenomenon occurs, the voltage cannot be recovered with 1C charging, and further analysis by professional technicians is required.
4) It is recommended that customers choose batteries with protective electronic components or integrated circuits such as fuses, temperature switches, etc. destroy).
5) It is recommended that customers pay attention to the distance between spot welding current and welding pins.
What happens if the battery/battery pack cannot be charged?
1) Check whether the battery or battery pack is a zero voltage, high internal resistance battery;
2) Check the connection of the battery pack and whether the electronic components and protection circuits are abnormal;
3) Check whether the charging equipment or charging circuit has charging voltage/current output in the charging state;
4) Whether the ambient temperature is too high and the charging efficiency is low (the optimal temperature should not exceed 40°C);
Approach:
1) Understand the specific usage and usage conditions of the battery by the customer;
2) Take the same type of battery and multimeter (current gear) in series into the circuit for charging, and judge whether the charging equipment is normal according to the charging current value.
3) Repeat the analysis and processing of the zero voltage steps of the single battery;
4) It is recommended that customers choose charging equipment or charging circuits with better stability;
What happens when the battery/battery pack fails to discharge?
Phenomenon: After charging, the device cannot work, and the open-circuit voltage of the battery pack does not change or changes little.
1) Check whether the battery/battery pack has zero voltage, high internal resistance battery;
2) Whether the electronic components and protection circuits inside the battery pack are damaged;
3) Check whether the discharge circuit of the equipment is normal.
Approach:
1) Connect the device with a fully charged battery/battery pack of the same type to see if the device works normally;
2) Use a multimeter to check whether the electronic components and protection circuits inside the battery are normal.
3) Repeat the analysis and processing of the zero voltage steps of the single battery;
4) If the discharge circuit of the electrical appliance is abnormal, it is recommended that the customer repair and replace the electrical appliance in time;
5) If the customer does not modify the battery pack by himself, specialized technical personnel are required for further analysis.
What are the reasons that may lead to the shortening of the service life of the battery?
1) Whether the customer’s charger or charging circuit matches the battery, and whether the output voltage/current is stable;
2) Whether the battery/battery pack is used according to SPEC requirements (such as battery usage and storage environment, etc.);
3) Whether the type of battery used by the customer is consistent with the customer’s equipment requirements.
4) Whether there is continuous overcharge or overdischarge of the battery/battery pack;
Approach:
1) Understand the specific usage of the battery;
2) Check the nominal rated current and voltage of the chrome plate of the charger;
3) Use a multimeter to connect the battery to the circuit to charge, and check whether the charging current is too large.
4) It is recommended to use a more stable charger or charging circuit that matches the battery/battery pack and a battery that matches the device;
5) It is recommended that customers use batteries/batteries as required, and try to avoid overcharging, reverse charging or overdischarging;
What is overcharge? What are the adverse consequences of overcharging? How to avoid it?
Theoretically, the Li-ion battery is charged at a constant current and constant voltage at a certain rate. When the charging is converted to constant voltage 4.2V charging, and the current in the charging circuit is 0.01C, the constant voltage charging state is still in progress, which is regarded as for overcharging.
Overcharging may lead to leakage, deformation, fire, and explosion after constant voltage failure as the charging voltage reaches a certain level (generally the limit is 6.0V), which is one of the main reasons for damaging the performance of the battery.
Adding PCB board protection outside the battery, or setting up a protection circuit and/or a time limit device in the charger (that is, the charging limit is 2.5 hours) to prevent the battery from overcharging can achieve the effect of prevention and protection.
What is over-discharge? What are the adverse consequences of over-release? How to avoid it?
The battery discharges at a constant current at a certain rate. When the battery voltage reaches 2.75V, the discharge state continues, which is overdischarge.
Over-discharge may lead to leakage, zero voltage and negative voltage, which is one of the main reasons for impairing battery performance.
Add a PCB board outside the battery or design a protection circuit and/or a time limit device in the charger to prevent overdischarge.
Under what circumstances will the battery explode? How to prevent?
There are several reasons for a battery to explode:
1) The external short circuit exceeds the endurance limit of the battery;
2) Overcharging. The charging voltage exceeds the limit value (generally no more than 6V);
3) The circuit board fails;
4) The temperature is too high (over 150℃);
What are the factors that cause the battery to short circuit? What are the consequences?
1) The external conductor is directly connected to the positive and negative poles of the battery;
2) The internal (micro) short circuit is caused by the external impact force of the battery during assembly;
3) The internal structure is poor (for example, the positive and negative electrodes are connected after the pole acne pierces the diaphragm)
If the outside of the battery comes into contact with any metal conductor, it may cause an external short circuit. An external short circuit of Li-ion batteries may cause deformation of the casing, leakage, fire, or even explosion. Because the temperature of the internal electrolyte rises, the internal pressure rises, and the rise in internal pressure will break the safety valve of the battery. If the safety valve fails, it will cause an explosion.
Keheng New Energy’s Range Of Products
- 100AH 12V Low Temperature Heating Enable
- Lithium Battery Cell
- Lithium Battery Pack
- Escooter/Ebike Battery
- 12V/24V Lifepo4 Battery
- Portable Power Station
- ESS Energy Storagy Systems
- Deep Cycle Batteries With BMS
- Low Temperature 24V 60AH Battery
Recommended reading
What Are The 11 Best Deep Cycle Marine Batteries?