Most people know the lithium battery have long lifespan and fastest-charging characteristic. But What is lithium ion battery? What is the advantage of lithium technology compare to lead acid battery? How long will a lithium battery last? Here is the Knowledge that you may want to know. Let’s dive in!
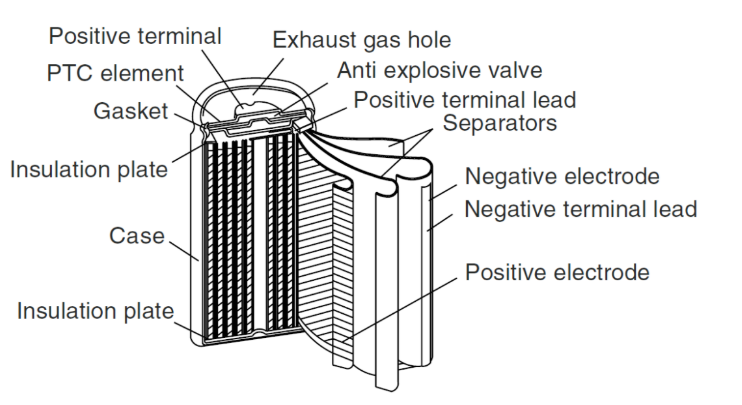
What Is A Lithium-Ion Battery?
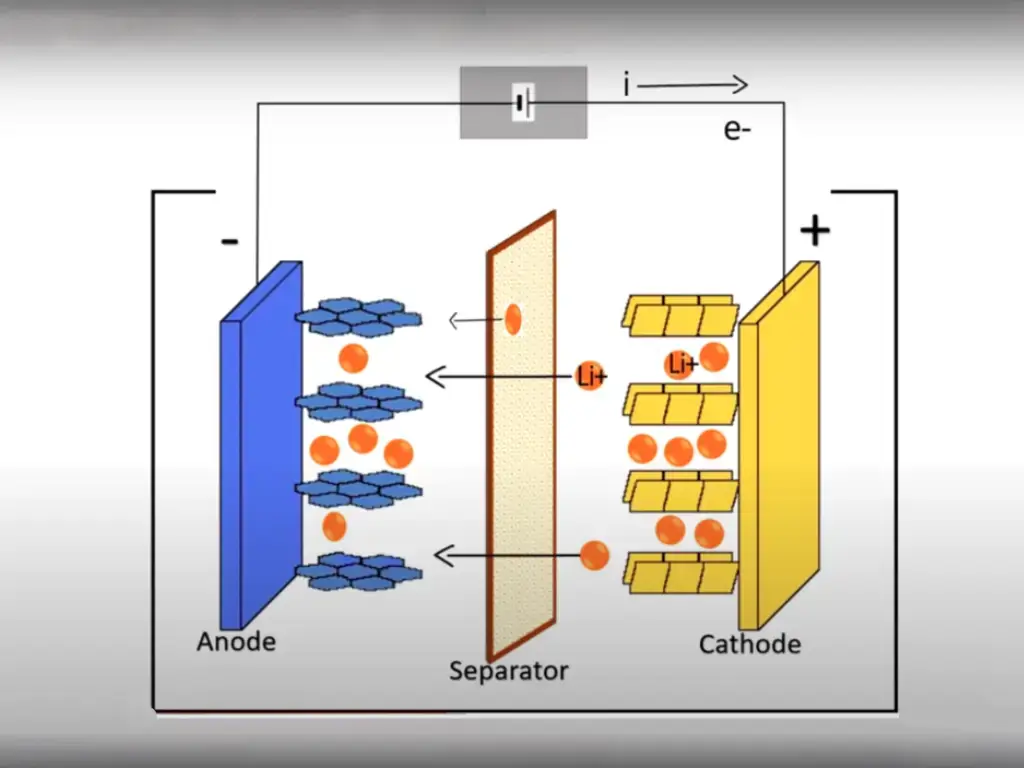
Lithium-ion batteries are mainly composed of four materials: positive electrode material, negative electrode material, separator, and electrolyte!
“Lithium battery” is a type of battery that uses lithium metal or lithium alloy as the negative electrode material and uses a non-aqueous electrolyte solution. In 1912, the lithium metal battery was first proposed and studied by Gilbert N. Lewis. In the 1970s, M. S. WhitTIngham proposed and began to study lithium-ion batteries. Due to the very active chemical properties of lithium metal, the processing, storage and use of lithium metal have very high environmental requirements. Therefore, lithium batteries have not been used for a long time. With the development of science and technology, lithium batteries have now become the mainstream. Lithium batteries can be roughly divided into two categories: lithium metal batteries and lithium ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries do not contain lithium in the metallic state and are rechargeable. The fifth generation of rechargeable batteries, lithium metal batteries, was born in 1996, and its safety, specific capacity, self-discharge rate and performance-price ratio are better than lithium-ion batteries.
In 1970, Exxon’s M.S. WhitTIngham used titanium sulfide as the positive electrode material and metal lithium as the negative electrode material to make the first lithium battery. The positive electrode material of lithium battery is manganese dioxide or thionyl chloride, and the negative electrode is lithium. After the battery is assembled, the battery has voltage and does not need to be charged. Li-ion batteries are developed from lithium batteries. For example, the button cells used in cameras in the past are lithium batteries. This kind of battery can also be charged, but the cycle performance is not good. Lithium crystals are easily formed during the charging and discharging cycle, resulting in a short circuit inside the battery. Therefore, charging of this kind of battery is generally prohibited.
In 1980, J. Goodenough discovered that lithium cobalt oxide can be used as a cathode material for lithium-ion batteries.
In 1982, R.R.Agarwal and J.R.Selman of the Illinois Institute of Technology (Illinois Institute of Technology) discovered that lithium ions have the characteristics of intercalating graphite, which is fast and reversible. At the same time, the safety hazards of lithium batteries made of metal lithium have attracted much attention. Therefore, people have tried to use the characteristics of lithium ions embedded in graphite to make rechargeable batteries. The first usable lithium-ion graphite electrode was successfully trial-produced at Bell Laboratories.
In 1983, M. Thackeray, J. Goodenough and others found that manganese spinel is an excellent cathode material, with low price, stability and excellent electrical conductivity and lithium conductivity. Its decomposition temperature is high, and its oxidizing property is much lower than that of lithium cobalt oxide. Even if a short circuit or overcharge occurs, the danger of burning and explosion can be avoided.
In 1989, A.Manthiram and J.Goodenough found that a positive electrode with a polymeric anion would produce a higher voltage.
In 1992, Sony Corporation of Japan invented a lithium battery with a carbon material as the negative electrode and a lithium-containing compound as the positive electrode. During the charging and discharging process, there is no metal lithium, only lithium ions. This is a lithium ion battery. Subsequently, lithium-ion batteries revolutionized the face of consumer electronics. Such batteries using lithium cobalt oxide as the positive electrode material are still the main power source for portable electronic devices.
In 1996, Padhi and Goodenough found that phosphates with an olivine structure, such as lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), are safer than traditional cathode materials, especially high temperature resistance, and their overcharge resistance far exceeds that of traditional lithium-ion battery materials. Therefore, it has become the current mainstream lithium battery cathode material for high current discharge. Throughout the history of battery development, we can see three characteristics of the current world battery industry development. One is the rapid development of green and environmentally friendly batteries, including lithium-ion batteries, nickel-hydrogen batteries, etc.; the second is the transformation of primary batteries into batteries, which is in line with sustainable development. Development strategy; third, the battery is further developed in the direction of small, light and thin. Among commercial rechargeable batteries, lithium-ion batteries have the highest specific energy, especially polymer lithium-ion batteries, which can achieve thinning of rechargeable batteries. Because lithium-ion batteries have high volume specific energy and mass specific energy, are rechargeable and pollution-free, and have three major characteristics of the current battery industry development, they have grown rapidly in developed countries. The development of telecommunications and information markets, especially the extensive use of mobile phones and notebook computers, has brought market opportunities for lithium-ion batteries. The polymer lithium ion battery in the lithium ion battery will gradually replace the liquid electrolyte lithium ion battery with its unique advantages in safety, and become the mainstream of the lithium ion battery. The polymer lithium-ion battery is known as “the battery of the 21st century”, which will open up a new era of storage batteries, and the development prospect is very optimistic.
How to build a lithium ion battery?
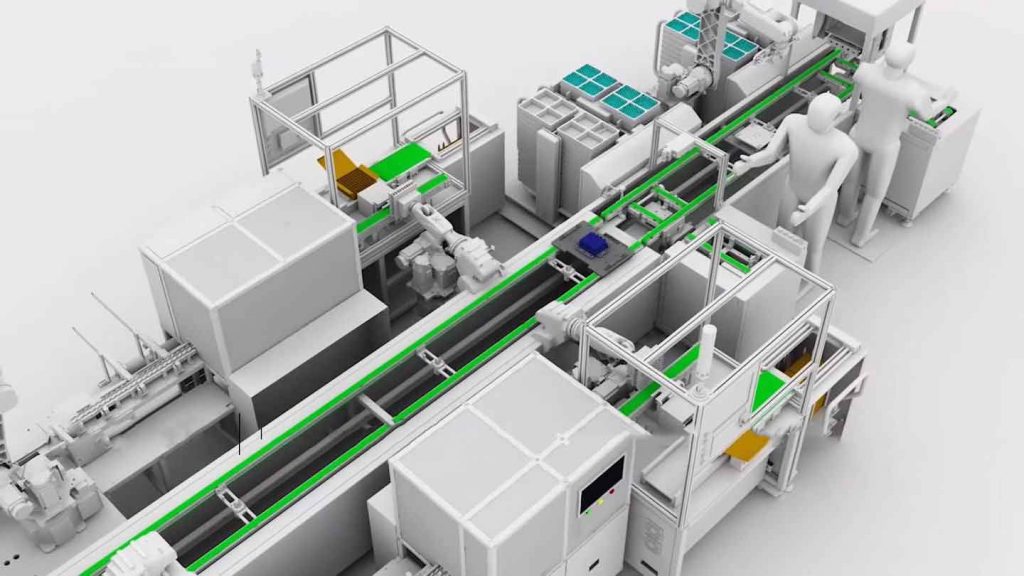
firstly, Lithium battery material composition
Four main materials: positive electrode material, negative electrode material, diaphragm, electrolyte
Auxiliary materials: NMP, copper foil, aluminum foil, aluminum shell cover, conductive agent, adhesive, other (EMD), etc.
Second, the production process
The manufacturing process of lithium batteries can be divided into four main processes: electrode preparation, cell assembly, activation detection and battery assembly. Among them, the electrode production also includes the production of positive electrode and negative electrode, and the main links include the steps of batching, stirring, coating, rolling, slitting, and tabs.
Third, Equipment required for production
According to the production process of lithium-ion batteries, lithium battery equipment can be mainly divided into front-end equipment, mid-end equipment and back-end equipment.
The front-end equipment is mainly for the electrode production process, including vacuum mixers, coating machines, roller presses and slitting machines. The coating process requires that the stirred slurry is evenly coated on the metal, and the thickness is accurate to less than 3 μm. It is necessary to ensure that there is no burr on the surface of the slice, otherwise it will have a great impact on the subsequent process. Therefore, front-end equipment is the core equipment of battery manufacturing, which is related to the quality of the entire production line.
The mid-end equipment mainly covers the cell assembly process, mainly including winding machines or lamination machines, cell shelling machines, liquid injection machines, and sealing and welding equipment.
The back-end equipment mainly covers processes such as cell activation and formation, capacity distribution detection, and assembly into battery packs. Relatively speaking, the middle and back-end equipment such as shell, sealing, testing and other machines are relatively simple, and the technical requirements are not high.
What is the application of lithium battery?
It is mainly divided into three parts: digital, power and energy storage.
Digital categories: mobile phones, tablets, notebook computers, electric toys, MP3/MP4, earphones, power banks, model aircraft, mobile power supplies, etc.
Power category: mainly refers to electric vehicles, Glof carts, RVs, Marine machine, automated guided vehicles (AGVs) , Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) , electric bicycles, etc.
Energy storage: Mainly used in base station power supply, clean energy storage, grid power storage, home solar storage system, etc.
It is believed that lithium batteries will be more widely used in the future



3 thoughts on “What is lithium ion battery?”
Your article gave me a lot of inspiration, I hope you can explain your point of view in more detail, because I have some doubts, thank you. 20bet
Hello,
Thank you for your kind words! I’m glad to hear that my article has inspired you. I’d be happy to provide further clarification on my points of view to address any doubts you may have.
Please feel free to let me know which specific aspects you’d like me to elaborate on, and I’ll do my best to explain in more detail.
Looking forward to assisting you further!
Best regards,
Your writing is a breath of fresh air! Your article is filled with original ideas and insights that are both thought-provoking and enjoyable. Your style is both unique and engaging, making your work stand out from the crowd. I’m looking forward to reading more from you!