Exploring the safety risks of series and parallel battery configurations is crucial in understanding the complexities involved. From overcharging to thermal runaway, these setups require meticulous management to ensure safe operation and longevity.
Implementing robust Battery Management Systems (BMS) is essential for monitoring and controlling voltage and current levels in each cell, mitigating risks associated with imbalances. By following safety tips and complying with legal frameworks, the safety and efficiency of lithium battery arrays can be maintained effectively.

Key Points
- Series and parallel battery configurations pose safety risks
- Overcharging can lead to imbalances and thermal events
- Thermal runaway is a critical risk in battery packs
- BMS is essential for monitoring and controlling battery cells
- Mismatched cells can compromise safety and performance
- Voltage and current imbalances can cause inefficiencies
- Safety tips include regular maintenance and proper ventilation
- Legal and regulatory frameworks ensure battery safety compliance
Safety Concerns with Series and Parallel Battery Configurations
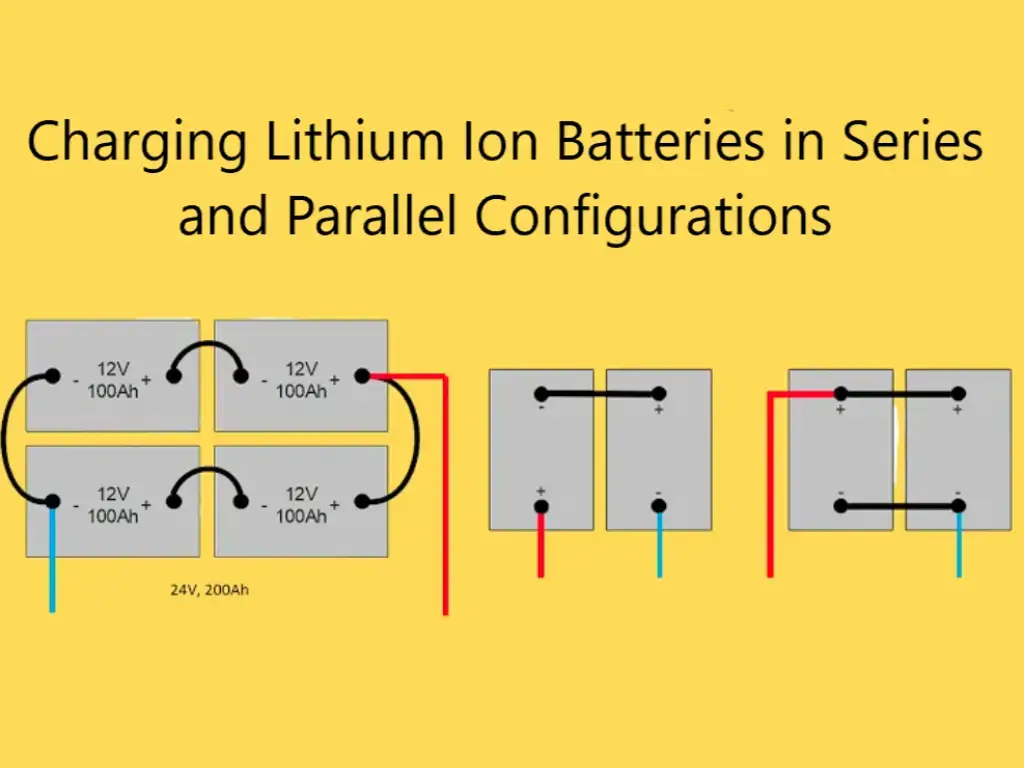
When discussing battery protection, it’s crucial to recognize the unique challenges posed by using the collection and parallel battery configurations. These setups are commonly used to boost voltage and ability in battery packs, as observed in electric motors and big-scale energy garage structures. In addition, they introduce several protection issues that must be rigorously managed.
In series configurations, batteries are related to cease to quit, increasing the percent’s voltage while preserving the equal capacity. Alternatively, parallel configurations connect the battery aspect by facet, expanding the potential while maintaining an unmarried cell’s voltage. Each setup can substantially modify the electric dynamics of battery operation, leading to expanded risks if no longer adequately controlled.
| Configuration type | Voltage trade | Ability change | Not unusual uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Series | Increases | Unchanged | Electric cars, portable electronics |
| Parallel | Unchanged | Will increase | Strength garage systems, backup power materials |
One of the number one concerns with these configurations is the opportunity for choppy charging and discharging. In a sequence setup, if one battery in the chain has a different price degree or deteriorates faster than others, it can lead to over-voltage situations on weaker batteries, degrading them and potentially inflicting failure. Parallel preparations can suffer from comparable issues, wherein imbalances in modern-day float can lead to cells being overcharged or discharged beyond their secure operational limits.
Moreover, the complexity of handling more than one battery stressed out together will increase the probability of voltage and current imbalances. These imbalances can stress the battery cells and result in untimely failure or, in extreme instances, catastrophic results with thermal runaway, wherein immoderate warmth ends in a damaging response in the battery percent.
Consequently, using sturdy battery control structures (BMS) is vital to screen and manipulate each cell’s voltage and present day, ensuring all work within safe limits. Such structures are crucial for mitigating the risks related to collection and parallel battery configurations and maintaining the longevity and safety of the battery p.C..
Ultimately, it is crucial to be aware that even as series and parallel configurations permit advancements in lots of technology, they require meticulous design and maintenance to ensure safety. Those setups are not inherently risky but can become so without proper precautions.
Risks of Overcharging in Series and Parallel Battery Setups
When discussing the safety of battery configurations, the dangers related to overcharging cannot be overstated. Overcharging in each series and parallel battery setups poses extensive risks that can lead to battery failure and, in severe instances, protection incidents. Information on these risks is vital for the secure operation of battery systems.
In series configurations, batteries are linked end-to-stop to grow the voltage. The primary risk here is that if one battery inside the series expenses faster than the others, it can become overcharged while the others have not but reached full ability. This imbalance can cause the overcharged battery to degrade faster, potentially leading to leakage or thermal activities.
Conversely, batteries are related aspect-by means of facet to boom capacity and output current in parallel configurations. Here, the hazard of overcharging arises if one battery has a barely better natural rate recognition price. Such disparities can cause a few batteries within the array to be pushed beyond their voltage thresholds while others are still charging, growing a comparable potential for harm and dangerous conditions.
Both scenarios underscore the importance of sturdy Battery control systems (BMS). A properly tuned BMS actively balances the fee across the batteries, mitigating the dangers of overcharging in both collection and parallel setups. That is important to lengthen the battery p.C. And maintain secure operation conditions.

It is also essential to note that the best batteries are vital in how inclined the setup is to overcharge. Batteries with excessive production standards and strict excellent management are less likely to have tremendous variances in rate reputation, which reduces the risks associated with overcharging in each series and parallel preparations.
Therefore, regular maintenance assessments, the correct configuration, and the usage of advanced BMS technology are essential practices to save you the overcharging of batteries in any setup, safeguarding each the functional integrity of the battery % and the safety of its operational surroundings.
Thermal Runaway Potential in Battery Packs
Thermal runaway represents a crucial hazard element in both series and parallel battery configurations. This phenomenon occurs when an increase in battery temperature ends in a further boom in temperature, regularly ensuing in a self-sustaining, unfavorable cycle. Especially while batteries are linked in series or parallel, the threat of thermal runaway may be exacerbated if one cell fails and triggers excessive warmness in nearby cells.
The heat generated via one failing cellular can propagate to adjoining cells, causing them to degrade and doubtlessly fail. This domino effect can lead to catastrophic consequences, including fires or explosions. The primary mechanisms at the back of thermal runaway include electrolyte decomposition, internal brief circuiting, and lively cloth degradation.
| Purpose of Thermal Runaway | Ability outcome |
|---|---|
| Electrolyte Decomposition | Release of flammable gases |
| Internal brief Circuit | Fast temperature boom |
| Energetic material Degradation | Structural disintegration in the mobile |
Elements including cell layout, battery management systems, and operational situations appreciably inspire the probability of thermal runaway. For example, high fee costs and extreme ambient temperatures can contribute to the onset of this situation. Moreover, batteries with poor first-rate management or lacking robust protection features are particularly susceptible to thermal runaway.
It is vital to contain complete battery control structures (BMS) that actively display and alter the conditions of every cell phone. Effective BMS can detect early signs of failure, including voltage fluctuations or bizarre temperature spikes, and might initiate corrective actions together with disconnecting affected cells to save you from the spread of thermal runaway.
Another aspect to remember when mitigating thermal runaway dangers is the selection of battery materials. Advanced electrode and electrolyte substances can enhance the thermal stability of the battery cells, presenting a better threshold before thermal runaway situations are reached.
Knowing the dynamics of thermal runaways and imposing stringent safety and control protocols can significantly decrease the risks associated with collection and parallel battery configurations. Even though continual research and development efforts are essential to similarly enhance the protection capabilities of battery technologies, ensuring more secure operation across a vast range of programs.
Importance of Proper Battery Management Systems
The protection and efficiency of battery arrays, whether arranged in collection or parallel configurations, depend on implementing robust Battery control structures (BMS). These structures are essential for monitoring and controlling each battery cell’s electric parameters and kingdom of health inside the percent. A BMS ensures that every cell functions within its unique electric thresholds, critical for preventing conditions that could lead to battery failure or hazardous conditions.
One of the primary features of a BMS is to adjust the charging manner to avoid overcharging or undercharging, each of which can degrade battery performance and durability. In collection configurations, the BMS meticulously balances the price across all cells to save you any single mobile from achieving a harmful voltage degree. That is equally critical in parallel setups, in which the BMS guarantees that the cutting-edge is flippantly distributed among all cells, protecting them from untimely wear and capability thermal occasions.
Besides voltage and cutting-edge regulation, a BMS also performs pivotal in temperature management. Batteries are liable to temperature fluctuations that can cause thermal runaway—a risky condition wherein an increase in temperature causes a similar increase in temperature, leading to an unfavorable cycle. A nicely-designed BMS actively video displays units the temperature of every cellular. It may initiate corrective measures, such as cooling the battery or lowering the fee modern, to maintain safe operation temperatures.
Moreover, the diagnostic capabilities of a BMS offer essential insights into the performance and fitness of the battery. By continuously assessing cell voltage, modern, temperature, and impedance records, a BMS can stumble on signs and symptoms of growing old or malfunctioning cells before they pose an extensive danger. This predictive upkeep no longer enables fending off screw-ups but also aids in optimizing battery utilization to increase its service lifestyles.
In the end, integrating a complete BMS in battery arrays is not simply an added feature but a necessity. The reliability of those structures in safeguarding against the inherent dangers related to series and parallel battery configurations is crucial for promoting each operational protection and sturdiness of the battery structures.
Effects of Mismatched Battery Cells in Configurations
Integrating mismatched battery cells in series and parallel configurations offers diverse safety and performance risks. When battery cells of differing capacities, nation of charge, or age are mixed, the general balance and performance of the battery p.C. It can be compromised. This section explores the critical issues related to such configurations.
Impact on Battery Overall Performance and Lifespan
Mismatched cells can result in a choppy distribution of price and discharge cycles, accelerating the degradation of specific cells while others stay underutilized. This imbalance now not only reduces the powerful lifespan of the battery percent but also impacts its overall performance reliability.
Dangers of Voltage and Contemporary Imbalances
In collection configurations, the entire voltage of the % is the sum of the voltages of all cells. If one mobile has a lower capability or an exceptional fee level, it could go through deeper discharge than its counterparts, potentially leading to over-discharge and harm. In parallel configurations, cells with better prices will discharge into people with decreased charge, leading to immoderate present-day go-with-the-flow, which can motivate overheating or thermal events.
| Configuration kind | Hazard | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Collection | Over-discharge of weaker cells | Cell damage decreases capability |
| Parallel | Excessive present-day float | Overheating, capability thermal runaway |
Prevention and control of Imbalances
A solid Battery control device (BMS) is vital to mitigate the risks of mismatched battery cells. A BMS actively monitors the voltage and contemporary of each cellular, ensuring balanced charging and discharging, which protects against the unfavorable consequences of cell mismatch. Moreover, periodic testing and preservation are encouraged to pick out and replace underperforming cells.
More advantageous monitoring techniques
Superior strategies, including impedance spectroscopy and thermal imaging, may be used to assess the fitness and features of male or female cells inside a %. These techniques assist in detecting early signs of mismatch or failure, preventing capability protection dangers.
In summary, while using mismatched battery cells in collection and parallel configurations can be economically tempting, the associated dangers often outweigh the initial savings. Right management through superior BMS technologies and regular maintenance routines are essential to ensure protection and efficiency in battery operations.
Voltage and Current Imbalances: Causes and Consequences
When configuring battery cells in series and parallel preparations, one should know the potential for voltage and contemporary imbalances. These imbalances are not merely inefficiencies but are primary assets of protection concerns that may critically affect the overall performance and durability of battery packs.
In series configurations, the overall voltage of the p.C. It is the sum of the voltages of all individual cells. If one cell has a decreased charge country or an exceptional capacity from its peers, it can grow to be the proscribing thing inside the battery string. This example forces the weaker cellular to discharge deeper and fee more unexpectedly than its counterparts, leading to multiplied degradation, decreased usual potential, and elevated risk of overcharging, which can provoke hazardous conditions, including thermal runaway.
Parallel configurations, while mitigating some voltage imbalance troubles by sharing the burden throughout multiple cells, introduce challenges with cutting-edge distribution. Cells in a parallel setup ought to preferably share the present day similarly. However, slight differences in cellular resistance or country of rate can cause unequal contemporary sharing. This results in some cells bearing more load than others, which can cause overheating and untimely failure.
The consequences of those imbalances are not restricted to cell harm. Voltage and cutting-edge discrepancies can also lead to the inefficient operation of the battery percent, lowering the gadget’s overall efficacy and power output. Furthermore, in intense cases, such imbalances can motivate protection hazards, including fires or explosions, especially if the battery management gadget (BMS) does not correctly detect and mitigate these situations.
A sturdy BMS is therefore critical for monitoring cellular voltages and currents, balancing the cells to save you these troubles, and ensuring the safe operation of battery packs in both collection and parallel configurations. Without such structures, the probability of unsafe occasions increases drastically, emphasizing the crucial nature of their position in battery protection and performance.
Safety Tips for Handling and Maintaining Battery Arrays
Protecting battery arrays, whether configured in series or parallel, demands adherence to specific preservation and coping with protocols. Rigorous safety requirements are crucial because of the inherent dangers related to these setups, voltage imbalances and the accelerated danger of thermal runaway.
Normal inspection and upkeep
Ordinary inspections are essential for detecting early damage symptoms or wear on batteries and connectors. Testing for visible defects, such as swelling, leakage, or corrosion, is crucial. These inspections should be carried out at periods exact with the manufacturer’s aid to ensure ongoing reliability and protection.
Ensuring proper airflow
Battery arrays must be saved in properly ventilated regions to prevent the buildup of gases that could potentially lead to explosions or fires. The spacing among batteries must also be sufficient for a good enough air stream.
Use of like-minded additives
While expanding or replacing elements of a battery array, ensure that every additive is well-matched. Mismatched cells can result in unequal charge and discharge costs, possibly compromising the entire device’s capability and safety.
Temperature control
Maintaining an ideal running temperature is essential to prevent thermal runaway and ensure the stability of battery cells. This will be controlled through environmental controls and, if vital, active cooling systems.
Implementation of Battery management systems (BMS)
A top-notch Battery control gadget (BMS) is crucial for monitoring cellular voltages, currents, and temperature. A BMS helps mitigate dangers by ensuring all cells in the array perform within safe limits and executing shielding actions if vital values are passed.
| Action | Motive | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspections | Hit upon bodily anomalies | month-to-month |
| Performance checks | Verify capacity and discharge costs | Bi-yearly |
| Environmental monitoring | Make certain the most useful temperature and humidity | Continuous |
Following those safety protocols now does not most effectively ensure the operational integrity of the battery arrays; however, it additionally appreciably complements consumer protection. By adhering to those hints, the risks associated with collection and parallel battery configurations can be effectively managed.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations for Battery Safety
In reaction to the complexities and capacity dangers related to series and parallel battery configurations, numerous criminal and regulatory frameworks have been established to ensure safety and compliance in the layout, testing, and deployment of battery systems. The focal point here is to shield both users and their surroundings from the risks posed by battery operations.
Regulatory bodies, including the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Fee (CPSC) and the ECU Union’s Battery Directive, play pivotal roles in setting safety standards. These standards are vital for mitigating risks related to overcharging, thermal runaway, and voltage imbalances, which might be extra pronounced in series and parallel configurations.
| Location | Regulatory body | Preferred or Directive | Key awareness location |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | CPSC | patron Product Protection Act | Standard product protection, in particular for customer electronics |
| European Union | European fee | Battery Directive (2006/66/EC) | Secure disposal, recycling, and chemical restrictions |
| International | IEC | IEC 62133 | Safety necessities for transportable sealed secondary cells |
For producers, adhering to these policies is about compliance and instilling customer confidence in battery technology. For example, the global Electrotechnical fee (IEC) specifies protection necessities underneath IEC 62133, which is pivotal for batteries used in portable gadgets. Compliance with such requirements ensures that battery packs can cope with the pressure and strain at some stage in ordinary and faulty situations without inflicting damage on users or belongings.
Moreover, neighborhood guidelines might also dictate extra safety measures to deal with demanding situations in areas vulnerable to precise environmental conditions. For instance, batteries may require more desirable mechanisms for warmth dissipation in hotter climates to save you from thermal runaway.
Ultimately, know-how and adhering to those felony and regulatory frameworks are crucial for anyone designing, manufacturing, and deploying battery structures. This ensures the safe operation of batteries is now not most effective in all applications and, additionally, the protection of the environment from the unsuitable disposal and breakdown of battery materials.
FAQs about Series and Parallel Battery Configurations
Are series and parallel batteries dangerous?
While series and parallel battery configurations are not inherently dangerous, they can pose risks if not properly managed. These setups can lead to safety concerns such as voltage imbalances, overcharging, and thermal runaway if not monitored and controlled effectively.
What are the safety concerns with series and parallel battery configurations?
Series configurations can lead to over-voltage situations on weaker batteries, while parallel configurations can suffer from imbalances in current flow. These issues can stress the battery cells and potentially cause failure or thermal runaway, primarily if not managed with a robust Battery Management System (BMS).
How can overcharging be a risk in series and parallel battery setups?
Overcharging in series setups can lead to imbalances in charging levels among batteries, causing degradation and potential failure. In parallel setups, overcharging can occur if one battery charges faster than others, leading to uneven charge distribution and potential thermal events.
What is a thermal runaway, and how does it relate to series and parallel battery configurations?
Thermal runaway is a dangerous phenomenon where an increased battery temperature leads to a self-sustaining cycle of further temperature rise. In series and parallel configurations, the risk of thermal runaway is heightened if one cell fails and triggers excessive heat in nearby cells, potentially causing catastrophic consequences like fires or explosions.
Why is a proper Battery Management System (BMS) crucial for series and parallel battery setups?
A BMS is essential for monitoring and controlling the voltage, current, and temperature of each battery cell in the pack. It helps prevent overcharging, voltage imbalances, and thermal runaway by ensuring all cells operate within safe limits and initiating corrective actions when necessary.
What safety tips should be followed when handling and maintaining battery arrays in series and parallel configurations?
Regular inspections, proper ventilation, using compatible components, temperature control, and implementing a BMS are essential safety tips for handling and maintaining battery arrays. These practices help prevent risks associated with voltage imbalances, overcharging, and thermal events in battery systems.
What legal and regulatory considerations are essential for ensuring battery safety in series and parallel configurations?
Adhering to safety standards set by regulatory bodies like the CPSC, EU Battery Directive, and IEC is crucial for manufacturers to ensure compliance and consumer confidence in battery technology. Local regulations may also dictate additional safety measures based on environmental conditions to address specific challenges.




3 thoughts on “Are Parallel and Series Batteries Dangerous? Safety Concerns Explored”
I just could not depart your website before suggesting that I extremely enjoyed the standard information a person provide for your visitors? Is gonna be back often in order to check up on new posts
Its like you learn my mind! You appear to know so much about this, such as you wrote the ebook in it or something. I think that you simply can do with some p.c. to power the message home a bit, but instead of that, that is magnificent blog. A great read. I’ll definitely be back.
As a Newbie, I am always exploring online for articles that can aid me. Thank you