Introduction to Lithium Ion Batteries
Lithium ion batteries have been the hallmark of the energy storage revolution since their introduction in the 1990s. These rechargeable batteries are famous for their high energy density, low self-discharge rate, and long lifespan. This has made them the preferred choice for powering electric vehicles, golf carts, RVs, and a wide range of electronic devices. On the other hand, adherence to the right charging practices is very important to guarantee the best performance, safety and long life of these batteries. In this extensive guide, we’ll explore the finer details of charging lithium ion battery correctly in order to provide you with advanced knowledge which will help you to get the most out of your battery.
Related Post: The Complete Breakdown: Pros and Cons of Lithium Ion Batterie
Why is Charging Properly Important?
It is important not only for safety reasons but also for maintaining the battery’s capacity and prolonging its life to properly charge lithium-ion batteries. Incorrect charging can have outcomes which can be the battery not reaching its full potential or wear out too early. For example, consistent undercharging may cause a condition called “memory effect” in which the battery “remembers” its reduced capacity and is no longer able to store the full amount of energy it was initially designed to store.
Moreover, the right charging guarantees all the cells in a battery pack are equally balanced as well. Out of balance cells can lead to a situation when some of the cells are overcharged while others are undercharged, which is undesirable and potentially dangerous (fire or explosion). It is therefore of primary importance to keep every cell within the pack properly charged so that the battery can be in good condition and efficiency.
Understanding Lithium Ion Battery Charging Principles
Lithium ion batteries operate based on the movement of lithium ions between the positive and negative electrodes during charging and discharging cycles. During a lithium ion battery charging process, lithium ions travel from the positive electrode (cathode) to the negative electrode (anode). This is done in the opposite direction of charging, with the ions flowing back to the anode at the time of discharge.
The lithium ion battery charging is not only the plugging until it is full. It is the process of managing the battery voltage, current, and temperature in equilibrium by the battery management system. The charging process typically consists of two stages: the continuous current (CC) stage and the continuous voltage (CV) stage. In the CC mode, the charger is set to deliver a constant current to the battery which is gradually increased until it reaches a voltage threshold established by the system. No sooner does the voltage reach this level, the charger switches to the CV mode, keeping the voltage constant while the current gradually decreases until the battery is fully charged.
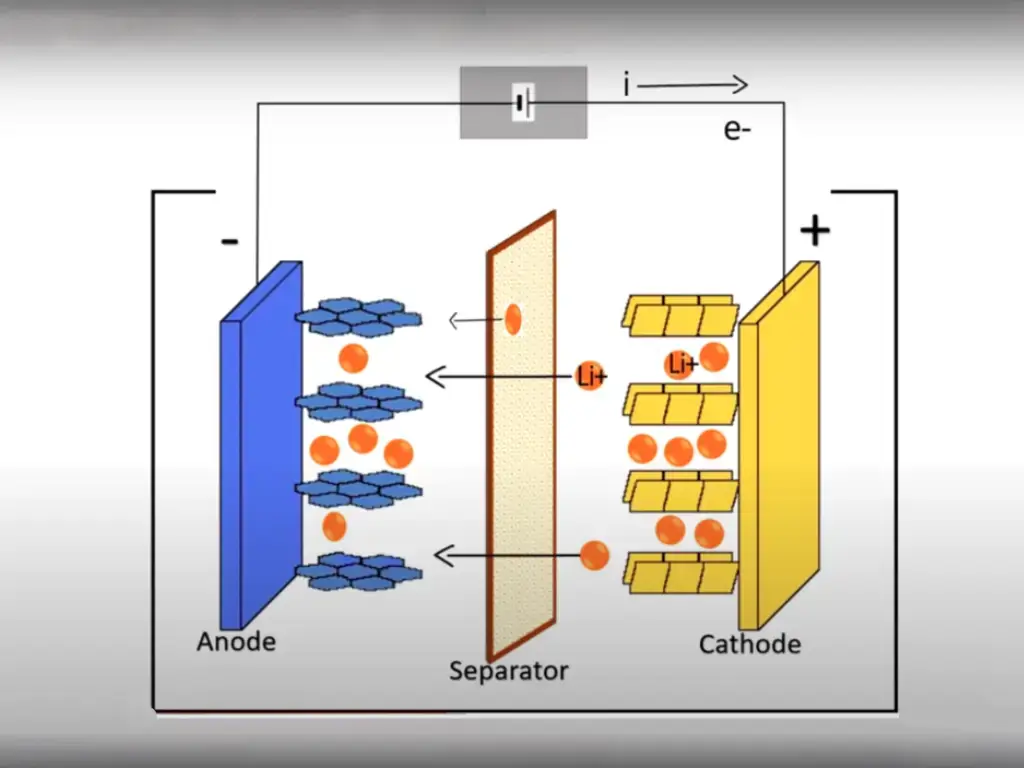
Lithium Ion Battery Charging Fundamentals
Charging Voltage
The charging voltage for lithium ion batteries has to be set at the right level to guarantee an efficient charging that does not damage the battery’s integrity. Usually the charging voltage is established by the battery types and by the cell arrangement. For lithium ion batteries, the normal charging voltage is 4.2 volts per cell, with a tolerance of ±0.05 volts, though some chemistries like lithium iron phosphate may have a lower voltage threshold of 3.6 volts per cell.
| Battery Chemistry | Typical Charging Voltage | Voltage Tolerance |
| Standard Lithium Ion (Li-ion) | 4.2 V | ±0.05 V |
| Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) | 3.6 V | ±0.05 V |
| Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO2) | 4.2 V | ±0.05 V |
| Lithium Manganese Oxide (LiMn2O4) | 4.1 V | ±0.05 V |
| Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (LiNiMnCoO2) | 4.2 V | ±0.05 V |
| Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (LiNiCoAlO2) | 4.2 V | ±0.05 V |
| Lithium Titanate (Li2TiO3) | 2.4 V | ±0.05 V |
Voltage fluctuation is one of the major issues for lithium-ion batteries, and even small deviations from the optimal range could cause capacity loss, shorten cycle life, and increase safety hazards. Charging the lithium ion battery should be monitored by regulating the voltage to avoid overcharging. While the battery can be used in this manner, exceeding these limits can cause it to become unstable, which may lead to the formation of metallic lithium dendrites that can pierce the separator and cause internal short circuits or even fires.
In addition, not charging a lithium ion battery sufficiently can also be harmful. Maintaining the voltage below the recommended level continuously may not give the battery a chance to hit the full capacity and thus may lead to reduced runtime and overall performance. Furthermore, extended undercharging may lead to the building of copper shunts, which can remain in the battery and drop its capacity.
Related Post: Do Lithium Batteries Leak? A Detailed Exploration of Battery Integrity
Charging Current for Lithium Ion Batteries
The right charging current for lithium ion batteries is chosen differently for different applications and for the design of the battery itself. The safety and effectiveness guideline is to charge at a rate that is neither too high nor too low and prevent excessive heating. For example, a charge current of a large battery pack varies from 0.5 C to 1 C, where C is the battery’s capacity in ampere-hours. Therefore, the charging current for a battery pack with a capacity of 100 Ah would be between 50 and 100 amperes.
Temperature Considerations During Lithium Ion Battery Charging
Temperature is a key element in the charging of lithium ion batteries. For instance, charging at too high temperature can fasten the degradation of the battery cells, while too low temperature can slow down the charging efficiency and even lead to lithium plating on the anode, which is in fact a form of permanent damage of the battery. The optimal charging temperatures are normally within the range of 10°C and 45°C. Temperature sensors as part of the BMS (battery management system) are very useful in monitoring and control of the temperature of safe charging conditions.
The Role of Battery Management Systems (BMS) in Battery Charging
A Battery Management System (BMS) is such a necessary condition for the health and safety of lithium ion battery packs, especially in bigger applications like electric vehicles and RVs. BMS monitors the voltages, currents, and temperatures of each cell in the battery pack. It makes sure that one cell of the battery is not overcharged or undercharged causing the battery to perform less or to have a shorter lifespan. Moreover, the BMS provides important safety features, like disconnecting the battery when the BMS detects abnormalities like short circuits, over-temperatures, or any other issues, which protects the battery and the equipment that is powered by it.

Step-by-Step Guide to Charging
Charging lithium ion batteries correctly involves several key steps to ensure safety and maximize battery life. Here’s a comprehensive guide to charging these batteries effectively:
Choose a compatible charger: Select a charger that is specifically designed for li ion batteries and matches the voltage and current requirements of your battery pack. Ensure that the charger is certified and meets the necessary safety standards.
Connect the charger: Carefully connect the charger to your battery pack, ensuring that the polarity is correct. Most chargers have clear markings for the positive and negative terminals. Double-check the connections to avoid any short circuits or reverse polarity.
Set the charging parameters: If your charger allows for adjustable settings, set the charging voltage and current according to the battery manufacturer’s recommendations. For most lithium ion batteries, the charging voltage should be 4.2V per cell, and the charging current should be between 0.5C and 1C.
Initiate the charging process: Turn on the charger and allow it to begin the charging process. The charger should automatically detect the battery pack and apply the appropriate charging voltage and current.
Monitor the charging progress: Keep an eye on the charging progress, which is usually indicated by LED lights or a display on the charger. Most chargers will show the current state of charge and provide feedback on the charging status. If you notice any abnormalities, such as excessive heat or unusual voltage readings, stop the charging process immediately.
Avoid overcharging: Once the battery pack reaches its full charge capacity, the charger should automatically switch to a maintenance or trickle charge mode to prevent overcharging. However, it’s still a good practice to disconnect the charger once the charging process is complete to avoid any potential issues.
Store the battery properly: After charging, if you don’t plan to use the battery pack immediately, store it in a cool, dry place away from extreme temperatures. Lithium ion batteries should be stored at around 50% state of charge for optimal long-term storage.
Charging Lithium Ion Batteries in Series and Parallel Configurations
When dealing with larger battery packs, such as those used in electric vehicles or energy storage systems, lithium ion batteries are often connected in series, parallel, or a combination of both configurations to achieve the desired voltage and capacity. Charging these battery packs requires special considerations to ensure optimal performance and safety.
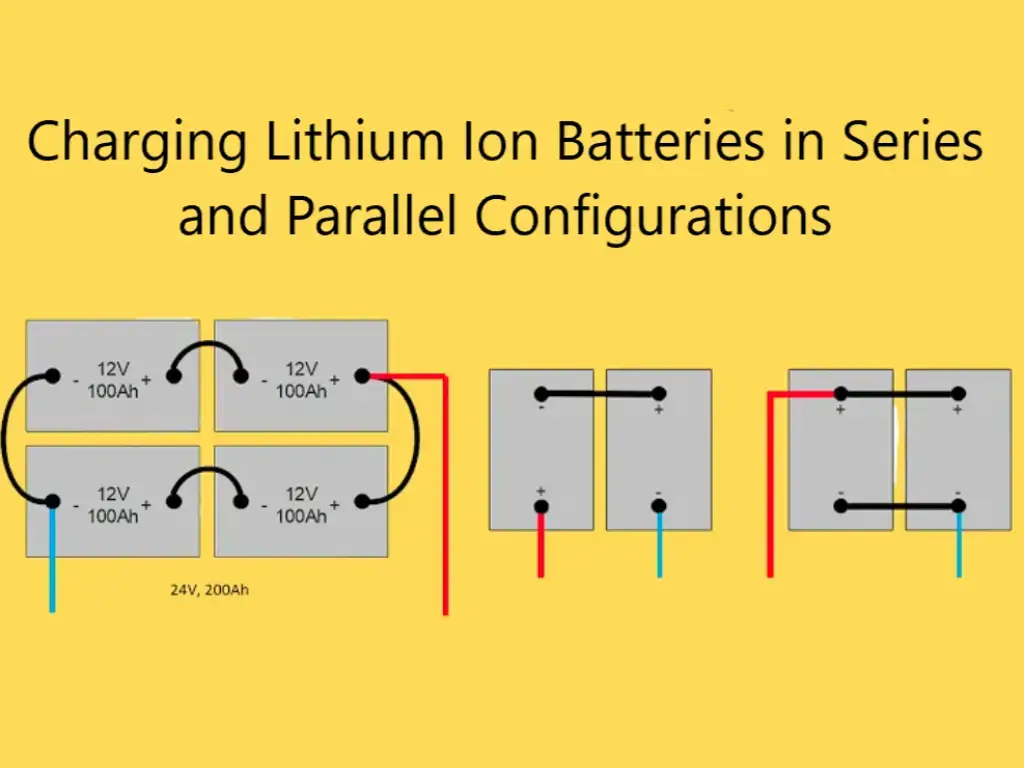
Series Charging Considerations
In a series configuration, lithium ion batteries are connected in a chain, with the positive terminal of one battery connected to the negative terminal of the next. This arrangement increases the overall voltage of the battery pack while maintaining the same capacity as a single cell.
When charging lithium ion batteries in series, it’s crucial to ensure that each cell in the series string reaches the same voltage level. If one cell charges faster or slower than the others, it can lead to an imbalance in the pack, causing overcharging or undercharging of individual cells. This imbalance can result in reduced performance, accelerated aging, and potential safety hazards.
To mitigate these issues, use a battery management system (BMS) that can monitor and balance the voltage of each cell in the series string. The BMS will ensure that all cells charge and discharge evenly, preventing any single cell from being stressed beyond its limits.
Parallel Charging Considerations
In a parallel configuration, lithium ion batteries are connected with their positive terminals joined together and their negative terminals joined together. This arrangement increases the overall capacity of the battery pack while maintaining the same voltage as a single cell.
When charging lithium ion batteries in parallel, the main concern is ensuring that the current is distributed evenly among all cells. If one cell has a higher internal resistance or a lower capacity than the others, it may charge faster or slower, leading to an imbalance in the pack.
To address this issue, use a charger that can provide sufficient current to charge all cells in the parallel configuration simultaneously. The charger should also have built-in safety features, such as overcharge protection and temperature monitoring, to prevent any single cell from being stressed beyond its limits.
In addition, it’s essential to use cells with closely matched capacities and internal resistances when constructing a parallel battery pack. This will help ensure that the cells charge and discharge at similar rates, minimizing the risk of imbalance and potential safety hazards.
How to Charge Lithium Ion Batteries for Long-Term Storage
When preparing lithium ion batteries for long term storage, it’s important to charge them to about 50-60% of their total capacity. This level of charge helps maintain battery health over time and prevents degradation linked to either fully charging or deeply discharging the batteries. Store the batteries in a cool, dry place, ideally at a stable temperature of around 10-20°C to further protect their longevity.
FAQ on Charging Lithium Ion Batteries
Q: How often should I charge my lithium ion battery?
A: You can charge your lithium ion battery whenever it’s convenient, as they don’t suffer from the “memory effect” that older battery technologies did. However, try to avoid regularly charging to 100% or discharging below 20% to minimize stress on the battery.
Q: Can I charge my lithium ion battery when it’s not completely empty?
A: Yes, you can charge your lithium ion battery at any state of charge. Unlike some older battery chemistries, lithium ion batteries do not suffer from the “memory effect,” which means they can be charged at any time without affecting their capacity or performance.
Q: How long does it take to charge a lithium ion battery?
A: The charging time depends on the battery’s capacity and the charging current. Typically, charging a lithium ion battery at a 1C rate (where the charging current equals the battery’s capacity) takes about 1-2 hours. However, lower charging currents will result in longer charging times.
Q: How long does it typically take to charge a lithium ion battery?
A: The charging time for a lithium ion battery depends on several factors, including the battery’s capacity, the charging current, and the initial state of charge. As a general rule, charging a battery from empty to full capacity with a 0.5C current will take approximately 2-3 hours. However, larger battery packs used in applications like golf carts or RVs may take longer due to their higher capacity.
Q: Can I charge my lithium ion battery with a higher current to speed up the charging process?
A: While charging with a higher current can indeed reduce the charging time, it’s generally not recommended. Charging with a current higher than the manufacturer’s specified range can lead to overheating, reduced capacity, and shorter battery lifespan. Always follow the recommended charging current for your specific battery.
Q: Can I charge my lithium ion battery in extreme temperatures?
A: It’s not recommended to charge lithium ion batteries in extreme temperatures, as this can lead to reduced performance, accelerated aging, and potential safety hazards. Try to maintain a stable charging temperature between 10°C and 45°C (50°F to 113°F).
Q: How can I tell if my lithium ion battery is fully charged?
A: Most chargers will indicate when the battery is fully charged, either through an LED indicator or a display message. Additionally, you can use a voltmeter to measure the battery’s voltage; a fully charged lithium ion cell should have a voltage of around 4.2V.
Q: Is it okay to leave my lithium ion battery on the charger after it’s fully charged?
A: Most modern lithium ion battery chargers are designed to automatically stop charging once the battery reaches 100% capacity, so leaving the battery on the charger should not cause any damage. However, it’s generally a good practice to remove the battery from the charger once it’s fully charged to avoid any potential issues.
Q: What is the best way to prolong the life of my lithium ion battery?
A: Avoid extreme temperatures, remove the battery from the charger once it’s fully charged, and keep it at a moderate charge level when not in use.
Q: Can I use a lithium ion battery charger designed for a different battery chemistry?
A: No, it’s crucial to use a charger specifically designed for your battery’s chemistry and capacity. Different lithium ion chemistries have different charging requirements, such as maximum voltage and current. Using an incompatible charger can lead to overcharging, undercharging, or other issues that can affect the battery’s performance and safety.
Conclusion
Charging lithium ion batteries correctly is essential for maintaining their performance, longevity, and safety. By understanding the key principles of lithium battery charging, such as using compatible chargers, monitoring voltage and current, managing temperature, and following best practices, you can ensure that your batteries operate at their best for years to come.
Remember to always prioritize safety when charging lithium ion batteries, and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations. Regularly inspect your batteries and chargers for any signs of wear or damage, and address any issues promptly to prevent potential hazards.
By staying informed about the best practices for charging lithium ion batteries and incorporating them into your routine, you can maximize the life and performance of your batteries while minimizing the risks associated with improper charging. Whether you’re using lithium ion batteries for electric vehicles, energy storage systems, or other applications, proper charging is key to unlocking their full potential.
Keheng: Trusted Lithium Battery Manufacturer
As a leading manufacturer, Keheng provides high-quality lithium ion battery solutions tailored for a wide range of applications. Our expertise ensures that every battery pack not only meets rigorous standards of safety and performance but also comes with the support needed to maintain those standards throughout the battery’s life. Trust Keheng for reliable, efficient, and safe lithium battery technology.



