When it comes to storing energy, it’s often a toss-up between Gel and Lithium batteries. As tech keeps moving forward, folks and big businesses alike are scratching their heads: which battery really fits the bill? In this post, we’re diving into the nitty-gritty of what each battery brings to the table—the advantages, the disadvantages, and everything in between. By the end, we’re hoping to give you a straight answer: gel vs lithium battery, which one truly steals the show?
What is a Gel battery?
A gel battery, part of the lead-acid category, uses a silica-based gel instead of the conventional liquid electrolyte found in standard lead-acid batteries. This thick, non-flowing gel reduces leakage risks and supports deeper discharges. The battery’s chemical reactions take place between the lead plates and this gel. Owing to their deep discharge potential, they’re often preferred for off-grid solar setups and marine applications.
What is a Lithium battery?
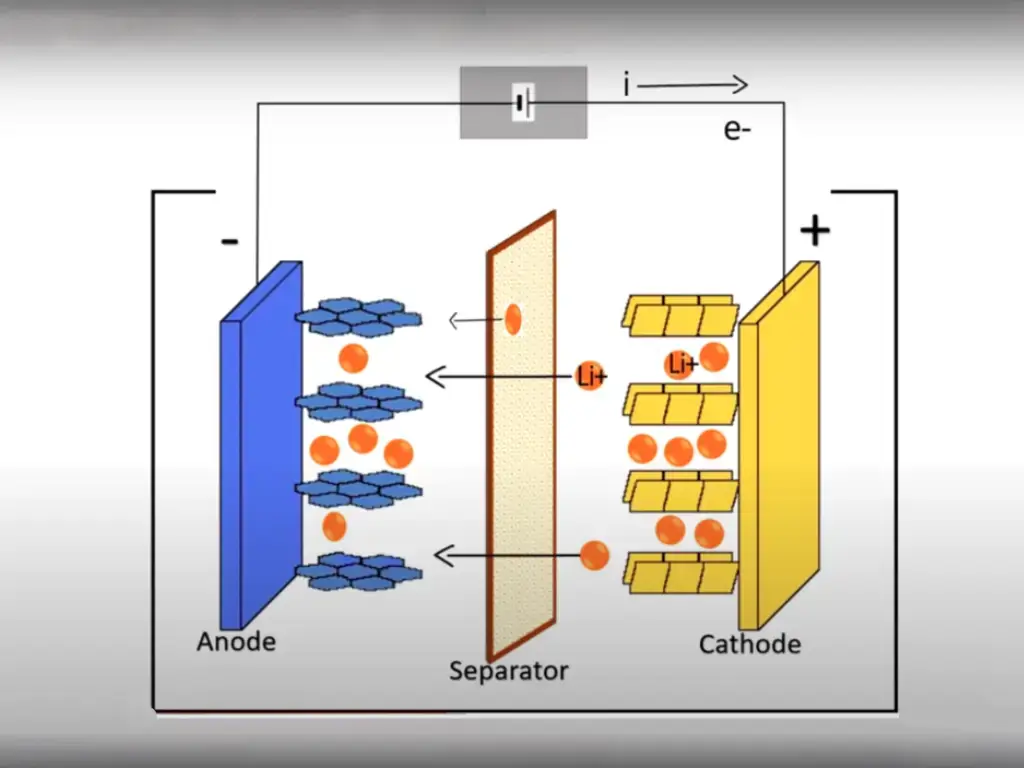
Lithium-ion batteries consist of an anode, cathode, separator, and a lithium-ion electrolyte. They operate by moving lithium ions between the anode and cathode during charge and discharge cycles. With their high energy density, light weight, and extended lifespan, they are favored in various applications, from smartphones to electric vehicles. Their excellent energy storage and efficiency often make them superior to other battery types. As renewable energy sources like solar power gain traction, lithium-ion batteries, particularly the lithium iron phosphate type, are emerging as top choices for energy storage.
What are the main differences: gel battery vs lithium
Lithium vs. Gel Batteries: Analyzing Energy Density & Efficiency
Energy density, quite straightforwardly, measures how much energy a battery can hold relative to its size or weight. This metric is paramount in industries where space and weight are premium commodities. With an impressive energy density that averages between 150-250 Wh/kg, lithium ion batteries provide the thrust behind the slim designs of modern smartphones and enable electric vehicles to cover remarkable distances on a solitary charge. On the flip side, gel batteries, although reliable, typically present an energy density between 30-50 Wh/kg. This often means a heftier design for the same storage capacity, posing challenges in space-constrained applications.
Now, turning our attention to energy efficiency – it’s all about how proficiently a battery can turn its stored energy into effective power. In this domain, lithium batteries again demonstrate their prowess, consistently showcasing efficiencies that often surpass the 90% mark. Picture this: For every 100 units of energy poured into a lithium battery, about 90 units are at your disposal, representing a minuscule energy wastage. Gel batteries, though sturdy, grapple with the inherent resistance of their thick gel electrolyte, and this sometimes results in efficiencies that hover between 80-85%.
For those who prioritize energy density and seamless efficiency, lithium batteries emerge as the undisputed leaders. They not only champion in storing a colossal amount of energy in a diminutive space but also in delivering it with unparalleled proficiency.
Depth of Discharge (DoD)
Depth of Discharge (DoD) — a significant determinant in the longevity and performance yield of a battery. Understood broadly, DoD unveils the percentage of a battery’s capacity that has been utilized. Lithium ion batteries promote a high DoD that stands typically between 80-90%. It’s akin to having a larger reservoir of energy at your disposal without the peril of diminishing its lifespan substantially. To put it into perspective, a lithium-ion battery can resiliently cater to high-demand settings, allowing the utilization of a vast chunk of its stored energy without significant repercussions on its longevity. Even in the scenario where it operates near its maximum DoD, the lithium-ion mechanism ensures a stable performance yield, consistently maintaining high energy output levels.
On the converse, gel batteries tend to offer a restricted DoD, generally advised to remain below 50%. This is not just a numerical limit but a reflection of the compromised utility in every cycle, with a substantive portion of the energy bank being virtually off-limits to avoid undue strain on the battery life.
It is increasingly transparent that when it comes to optimal DoD, lithium-ion batteries present themselves as a far more flexible and resilient choice, nurturing a balance between energy exploitation and longevity.
Related Post: What is Depth of Discharge? Everything You Need to Know
Lifespan and Durability of gel vs lithium battery
Lithium-ion batteries are pretty cool. They last a long time, often giving you around 2,000 to 3,000 charges before they start to wear out. That means they can keep going strong for over ten years in many cases, which is a great deal.
On the other hand, gel batteries are known for being tough cookies. They can handle rough conditions and don’t leak thanks to their gel makeup. But when it comes to lasting a long time, they usually give you a cycle life between 500 to 1,000 charges. So, while they’re durable, lithium-ion batteries take the cake in the long run.
Charging Dynamics: Speed, Efficiency, and Maintenance
Lithium-ion batteries are renowned for their rapid charging capabilities. They often reach up to 80% charge within just an hour which ensures minimal downtime. This quick boost is awesome, especially in industries where time is money.
On the other hand, gel batteries, while dependable, take their sweet time to charge up. The gel-like electrolyte is sensitive to high charge currents. They don’t like too much power all at once, so you gotta be patient with them, which often results in extended charging times.
Furthermore, lithium-ion batteries boast a notably low self-discharge rate. They barely lose any charge when sitting around. So, they’re always ready to roll when you need them.
Maintenance-wise, the advanced Battery Management Systems (BMS) in lithium-ion batteries offer an edge, providing automated cell balancing and protection. While gel batteries benefit from a leak-resistant design, their propensity for overcharging requires more attentive oversight.
So, if you’re all about swift charging, enduring efficiency, and low maintenance,lithium-ion batteries are a no-brainer. They’re modern tech wonders and super reliable.
Safety Concerns: Evaluating Risks and Precautions for Both Battery Types
Lithium-ion batteries once got a bad rap for getting super hot or even going up in flames. But hey, that’s mostly about the old-school ones. The newer kids on the block, especially the lithium iron phosphate ones, are way cooler – literally! They’re made up of stuff that doesn’t get all heated up easily.
Gel batteries? Oh, they’re rockstars when it comes to playing it safe. The gooey stuff inside doesn’t leak. But like everything, they’ve got their quirks. Charge ’em up too much and they might puff up like a balloon and, on a super rare occasion, go pop.
Both batteries have their ups and downs when we talk safety. But with all the techy magic happening in the lithium-ion world, they’re catching up, making sure we get the juice without the jitters.
Environmental Impact: Assessing the Eco-Footprint of Gel and Lithium Batteries
Whether it is a gel battery or a lithium battery, they should consider the environment. Lithium-ion batteries, due to their higher energy density and efficiency, often have a lower carbon footprint over their lifecycle, primarily when used in renewable energy systems like solar panels. However, mining lithium and other materials for these batteries does have environmental implications.
Gel batteries, being lead-acid types, involve lead, which poses environmental risks if not properly recycled. That said, the recycling infrastructure for lead-acid batteries is well-established, ensuring most get recycled.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment vs Long-Term Value
On the surface, lithium-ion batteries seem a bit more expensive. But the fact is not that. Even though you might shell out 20% more upfront for a lithium-ion battery compared to a gel one, the longer lifespan, higher efficiency, and deeper discharge depth mean that over 5 years, you’re looking at saving up to 30% per kWh.
Sure, gel batteries might seem like a cheaper option at first, but they can end up costing more in the long run with frequent replacements and more upkeep, thanks to their shorter life and less efficiency. So, if you’re thinking of long-term savings, going with lithium-ion batteries is often the smarter money moves. They pack a punch in performance and save you some serious cash over time.
Weight and Size Considerations: Portability and Installation Factors
With their higher energy density, lithium-ion batteries pack more power in a more lightweight package compared to gel batteries, making them a go-to choice for space and weight-sensitive applications like RVs or marine equipment.
Given their larger size, gel batteries could be a bit tricky to fit in places where space is at a premium.
Temperature Tolerance
Both battery types have their ideal temperature ranges. Lithium-ion batteries (including lifepo4 batteries) generally like it moderate and might see a dip in performance when it’s too hot or cold. On the other hand, gel batteries, thanks to their sturdy build, can endure a wider range of temperatures, but they might not be as efficient when the weather gets chilly.
Related Post: LiFePO4 Battery Temperature Range: Balancing Performance and Durability
Lithium vs Gel Battery, Which is Better?
| Lithium Battery | Gel Battery | |
| Pros | Lithium batteries provide ample energy in a compact size.They sustain many charge-discharge cycles with minimal capacity loss.They recharge quickly, minimizing downtime.Minimal energy loss during charging and discharging.Especially with lithium iron phosphate battery, which is chemically stable.They utilize a significant portion of their energy in each cycle. | Gel electrolyte reduces leakage risks, increasing safety.Their structure is built for lasting performance in tough applications.Gel batteries usually have a lower starting cost.They function efficiently across varied temperatures. |
| Cons | Higher initial expense, but often balanced by long-term value.Despite improvements, careful handling and charging are essential. | They are often larger than lithium batteries for similar energy output.They take more time to recharge due to their design.More energy losses during charge-discharge cycles.Much of their energy is reserved each cycle to maintain battery life. |
Looking at the latest tech trends and the obvious perks like how long they last, how much power they pack, and how efficient they are, it’s kinda clear that lithium-ion batteries are ahead of the game for most stuff. Now, don’t get me wrong, gel batteries are cool in their own way and they’ve got their own strong points. But if we’re talking about where the future’s headed, especially with all this green energy stuff popping up, lithium seems to be the go-to choice when we need something that’s gonna last and do the job right.
Diverse Applications of Each Battery Type
Choosing between gel and lithium-ion batteries isn’t just eeny, meeny, miny, moe; you gotta know what each is good at. Gel batteries? They’re your rock. If you’re off the grid with solar, they can take a beating, handling deep dives of energy use, like, around 50%. And if you’re sailing? They’re the real MVP, hardly needing a touch-up.
Alright, over to lithium-ion. Man, these things are everywhere! With their beefy energy storage, they’re the heart of almost every smartphone and laptop. Got an electric car? Chances are it’s rocking a lithium-ion battery that goes for 300 miles easy. And talking about clean energy storage? Lithium-ion, especially the lithium iron phosphate kind, is the next big thing, lasting longer and pulling off an awesome 80% energy dive. Breaking it down: lithium-ion seems to be the hot stuff now, but gel batteries aren’t going anywhere—they’ve got their own cool gigs.
Conclusion
The whole “gel vs lithium battery” discussion isn’t black and white. Sure, gel batteries have had our back for a long time, but when you look at what lithium-ion batteries bring to the table – like their power-packed performance and lasting power – it’s pretty clear they’re looking like the next big thing. As tech keeps evolving and we’re all about that green energy life, lithium-ion batteries just seem to be getting more and more of the spotlight in the energy storage world.
KH tech: Get a Free Quote
If you’re scratching your head over which battery is your jam, we at KH tech got your back. With our know-how in lithium-ion goodness, we’re here to steer you right. Give us a shout for a no-strings-attached quote, and let’s kickstart your energy journey together.



1 thought on “Gel vs Lithium Battery Showdown: Which Comes Out on Top?”
How much it holds is entirely down to the pressure tank, which can be any size you like and really doesn’t cost much to make bigger – just string a few extra standard tanks together, or make a large scale one, which isn’t particularly hard or expensive when you stay to low pressures. The moving parts that can wear out from use are the pump element not the tank, and that normal shop compressor pump is massively mass produced (not to mention that same pump will ship with tanks of a variety of sizes too – my compressor for instance has the 100L tank, but the same pump is available off the shelf with various sizes up to 200L bigger than that you get the next size up pump)…As for service life the half decent ones seem to keep going forever, I’ve seen ones older than I am that still work and have had lots of use – I assume less effectively than they used to as no amount of proper oiling and maintenance can negate all wear, but still they last a very very very long time if you look after them at all, and the most common point of failure does seem to be be the pressure tank being left full of water not the pump…