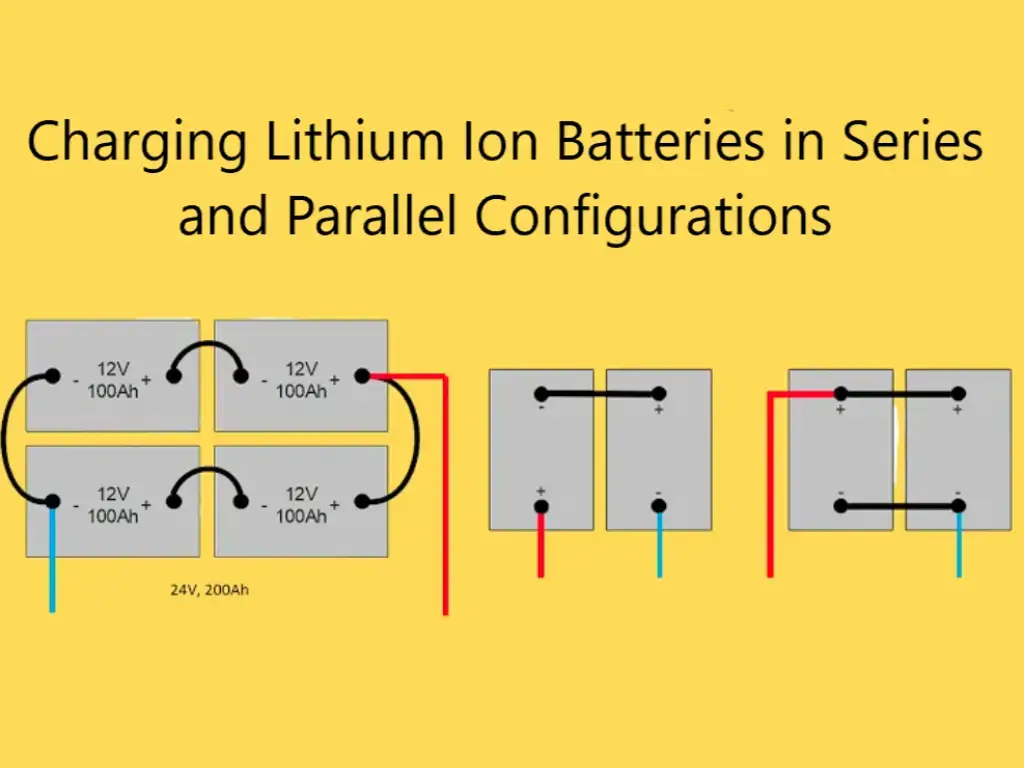
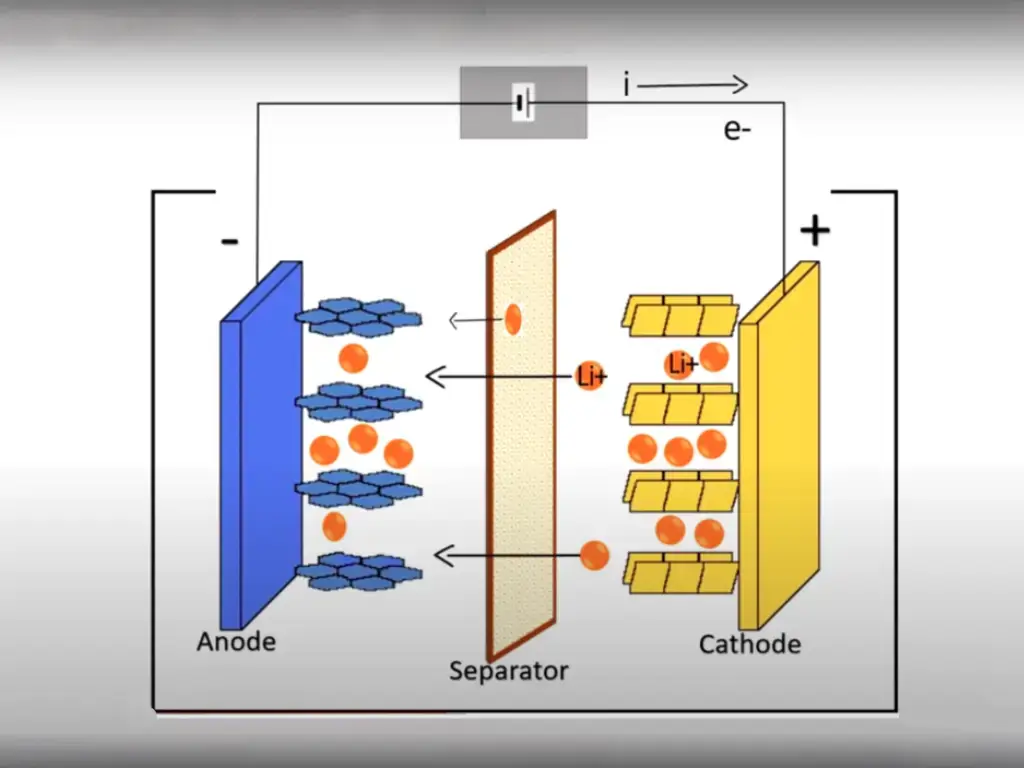
The Power Source Dilemma: Lifepo4 Batteries vs Gel Batteries
A Brief Overview of Battery Technologies

In today’s modern world, batteries play a crucial role in powering our everyday devices and applications. From smartphones to electric vehicles, the demand for reliable and efficient energy storage solutions has never been higher. Battery technologies have evolved significantly over the years, with various types catering to different needs and requirements.
Two prominent contenders in the realm of rechargeable batteries are LiFePO4 batteries vs Gel batteries. These technologies offer unique characteristics that make them suitable for specific applications.
LiFePO4 batteries are a type of lithium-ion battery known for their high energy density and excellent cycle life. The chemistry behind LiFePO4 batteries allows them to deliver stable power output over multiple charge-discharge cycles, making them ideal for applications that require long-term reliability.
On the other hand, Gel batteries utilize a gel electrolyte instead of a liquid one, providing enhanced durability and resistance to vibration and shock. This feature makes Gel batteries well-suited for use in environments where traditional lead-acid or lithium-ion batteries may struggle to perform optimally.
The Importance of Choosing the Right Battery for Specific Applications
Selecting the appropriate battery technology is paramount when it comes to ensuring optimal performance and longevity in various applications. Different devices and systems have distinct power requirements, operating conditions, and space constraints that dictate the choice of battery technology. For instance, in renewable energy systems such as solar panels or wind turbines, the ability to store excess energy efficiently is vital for maximizing overall system efficiency.
LiFePO4 batteries stand out in this scenario due to their high energy density and fast charging capabilities. Moreover, automotive applications like electric vehicles demand batteries that can provide sufficient power while being lightweight and compact enough not to compromise vehicle performance or range.
Here again, LiFePO4 batteries shine with their lightweight design and long cycle life compared to Gel batteries or traditional lead-acid counterparts. Making an informed decision based on factors such as energy requirements, space limitations, cost considerations, and environmental impact can significantly impact the performance and longevity of any given system powered by these advanced battery technologies.
LiFePO4 batteries VS gel batteries

Exploring the Chemistry and Structure of LiFePO4 Batteries
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries, also known as LFP batteries, are a type of lithium-ion battery that utilizes a cathode material composed of lithium iron phosphate. The unique chemistry of LiFePO4 allows for stable and efficient energy storage.
The structure of LiFePO4 cells consists of a lithium metal oxide cathode, an electrolyte solution, and an anode typically made of graphite. The key component, the lithium iron phosphate cathode, is what distinguishes these batteries from other lithium-ion variants.
Unveiling the Advantages of LiFePO4 Batteries
One remarkable advantage of LiFePO4 batteries is their high energy density, which refers to the amount of energy stored per unit volume or weight. This high energy density makes LiFePO4 batteries ideal for applications requiring long-lasting power in a compact size. Moreover, LiFePO4 batteries boast an impressive long cycle life compared to other battery types.
With thousands of charge-discharge cycles before significant capacity degradation sets in, these batteries offer durability and reliability over the long term. Another standout feature of LiFePO4 batteries is their fast charging capabilities.
Due to their unique chemistry and structure, they can efficiently absorb and release energy at a rapid rate without compromising performance or safety. This attribute makes them particularly suitable for applications where quick recharging is essential.
Additionally, despite their high energy density and fast charging abilities, LiFePO4 batteries maintain a lightweight and compact design. This lightweight nature makes them ideal for portable devices or electric vehicles where minimizing weight is crucial for maximizing efficiency and performance.
Overview of Gel Batteries
Explanation of Gel Battery Technology and Construction
Gel batteries, also known as gel cell batteries or sealed gel batteries, are a type of valve-regulated lead-acid (VRLA) battery. They are constructed using a gelled electrolyte that immobilizes the sulfuric acid in a gel form, making them maintenance-free and spill-proof.
The gel electrolyte typically consists of silica mixed with sulfuric acid to create a thick paste-like substance that surrounds the lead plates inside the battery. This unique construction allows for safe and reliable operation in various environments without the need for regular maintenance or monitoring.
Advantages of Gel Batteries
Maintenance-Free Operation
One of the key advantages of gel batteries is their maintenance-free operation. Unlike traditional flooded lead-acid batteries that require regular topping up with distilled water to prevent drying out, gel batteries do not need any maintenance once they are sealed during manufacturing. This makes them ideal for applications where access to the battery is limited or where routine maintenance is impractical.
Deep Discharge Capability
Gel batteries are designed to withstand deep discharges without compromising their performance or lifespan. They can be discharged to very low levels without causing damage to the battery, making them suitable for applications where deep cycling is common, such as in renewable energy storage systems or off-grid installations. This deep discharge capability ensures reliable power supply even under demanding conditions.
Resistance to Vibration and Shock
Gel batteries have excellent resistance to vibration and shock due to their construction with gelled electrolyte that immobilizes the components inside the battery. This feature makes them ideal for use in mobile applications such as marine vessels, RVs, or off-road vehicles where constant movement and rough terrain can cause traditional batteries to fail prematurely. The resilience of gel batteries against external forces ensures their longevity and reliability in challenging environments.
Suitable for High-Temperature Environments
Another significant advantage of gel batteries is their ability to perform reliably in high-temperature environments. The gelled electrolyte helps dissipate heat more efficiently compared to traditional flooded lead-acid batteries, reducing the risk of overheating and extending the battery’s lifespan. This characteristic makes gel batteries ideal for use in hot climates or applications where temperature control is limited, ensuring consistent performance even under extreme thermal conditions.
Energy Density: The Power Within
When it comes to energy density, LiFePO4 batteries outshine gel batteries with their ability to store energy more efficiently. LiFePO4 batteries have a higher energy density, meaning they can pack more power in a smaller space compared to gel batteries. This makes them ideal for applications where space is limited, such as in portable electronic devices or electric vehicles.
The high energy density of LiFePO4 batteries allows them to deliver consistent power output over a longer period, making them a reliable choice for demanding scenarios. On the other hand, gel batteries have a lower energy density compared to LiFePO4 batteries.
While they are still capable of storing energy effectively, their larger size and weight may be a limitation in certain applications where compactness and lightweight design are crucial. Gel batteries are commonly used in backup power systems or stationary applications where size and weight are not significant factors.
Cycle Life: Endurance Matters
In terms of cycle life, LiFePO4 batteries reign supreme over gel batteries with their exceptional longevity and consistent performance. LiFePO4 batteries can endure a significantly higher number of charge-discharge cycles compared to gel batteries, making them the preferred choice for applications requiring frequent use and deep cycling.
This extended cycle life not only provides cost savings in the long run but also ensures reliable performance over an extended period without degradation. Gel batteries, while durable in their own right, have a shorter cycle life compared to LiFePO4 batteries.
They may not be as suitable for applications that demand frequent cycling or deep discharges since their performance could deteriorate faster over time. However, gel batteries excel in scenarios where occasional deep discharges are expected without compromising their overall lifespan.
Charging Capabilities: Speeding Towards Efficiency
When it comes to charging capabilities, LiFePO4 batteries demonstrate faster charging speeds compared to gel batteries due to their unique chemistry and structure. LiFePO4 technology allows for rapid charging without compromising battery health or longevity, making them an efficient choice for applications that require quick turnaround times on recharging.
The fast-charging capabilities of LiFePO4 batteries contribute to overall system efficiency by minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity. Conversely, gel batteries have slower charging rates compared to LiFePO4 counterparts due to the nature of their construction and chemical composition.
While gel batteries can still be charged effectively within a reasonable timeframe, they may not match the rapid recharge speeds offered by LiFePO4 technology. This difference in charging capabilities should be considered when selecting the appropriate battery type for specific applications where quick recharging is essential.
Weight and Size: Compact Versatility
In terms of weight and size considerations, LiFePO4 Batteries emerge as the clear winner by offering a lightweight and compact design that enhances portability and versatility across various applications. Their smaller form factor makes them ideal for integration into portable devices or mobile equipment where space-saving solutions are critical without compromising on performance or capacity.
On the other hand, Gel Batteries tend towards larger sizes due to their construction requirements which include thicker plates which results into heavier weights as well . This could pose challenges especially in situations where weight constraints play a significant role such as in marine vessels or lightweight electric vehicles .
Despite this drawback , Gel Batteries do offer robustness which could be advantageous depending on application requirements . By considering these factors , It’s evident that choosing between Lifepo 04 Batteries vs Gel Batteries requires careful evaluation based on specific needs , ensuring optimal performance , efficiency ,and longevity tailored accordingto your application .
Renewable Energy Systems
Harnessing Sustainable Power with Advanced Battery Technology
In renewable energy systems such as C & I ESS, home battery backup, and marine ESS, the choice of lithium iron phosphate or colloidal batteries can have a significant impact on the efficiency and effectiveness of the entire system. LiFePO4 batteries are well-suited for renewable energy applications due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and fast charging capabilities. These qualities make them ideal for storing intermittent renewable energy sources like solar or wind power efficiently.
Gel batteries have also found a place in renewable energy systems for their resistance to vibration and shock, making them durable options for off-grid installations or harsh environmental conditions. However, LiFePO4 batteries are gaining prominence in this sector due to their ability to provide reliable power storage with minimal maintenance requirements.
As the world transitions towards sustainable energy solutions, LiFePO4 batteries are increasingly being integrated into renewable energy systems to maximize energy capture from sources like solar panels or wind turbines. Their advanced technology offers a more efficient way of harnessing clean power while ensuring long-lasting performance.
Marine Applications
Navigating Seas of Possibilities: Powering Boats & Yachts with Precision
When it comes to marine applications such as boats or yachts, selecting the right battery type is essential for ensuring durability and optimal performance in challenging maritime environments. In this context, both LiFePO4 batteries and gel batteries cater to specific needs based on their unique features. LiFePO4 Batteries:
– Lightweight design makes them ideal for marine vessels where weight considerations are crucial. – High tolerance to deep discharges ensures consistent performance over extended periods at sea.
– Fast-charging capabilities allow quick replenishment of power between voyages. Gel Batteries:
– Resilience against vibration makes them suitable for marine vessels exposed to rough seas. – Maintenance-free operation reduces upkeep requirements during long journeys.
– Ideal for use in high-temperature environments often experienced on boats. Ultimately when it comes down to marine applications these battery technologies offer distinct advantages tailored towards specific needs on watercraft like boats or yachts depending on factors such as weight considerations operating conditions maintenance requirements ensuring boaters can find an optimal solution that suits their individual requirements leading two enhanced experiences out at sea.
Environmental Impact
Recycling Considerations for LiFePO4 Batteries and Gel Batteries
When it comes to the environmental impact of batteries, recycling plays a crucial role in reducing waste and conserving resources. LiFePO4 batteries are known for their recyclability due to the valuable materials they contain such as lithium, iron, and phosphorus.
Recycling these batteries involves extracting these materials through specialized processes to be reused in the production of new batteries or other products. Gel batteries, on the other hand, also have components like lead and sulfuric acid that can be recycled but require careful handling due to their toxic nature.
Disposal Methods and Potential Environmental Risks
Improper disposal of batteries can lead to serious environmental risks such as soil and water contamination from toxic substances leaching into the ecosystem. LiFePO4 batteries are considered safer than gel batteries in terms of disposal since they do not contain hazardous materials like lead or acid.
However, both types of batteries should be disposed of responsibly through designated recycling centers or hazardous waste facilities to prevent environmental harm. Proper disposal methods include neutralizing acids, segregating battery types, and ensuring compliance with local regulations.
Conclusion
While both LiFePO4 batteries VS gel batteries offer unique advantages in terms of performance and durability, their environmental impact cannot be overlooked. By prioritizing recycling considerations and adopting responsible disposal methods, we can minimize the negative effects on our environment and promote sustainability in the battery industry.
Choosing eco-friendly options when it comes to energy storage solutions not only benefits the planet but also contributes to a cleaner future for generations to come. Let us strive towards a greener tomorrow by making informed choices today.