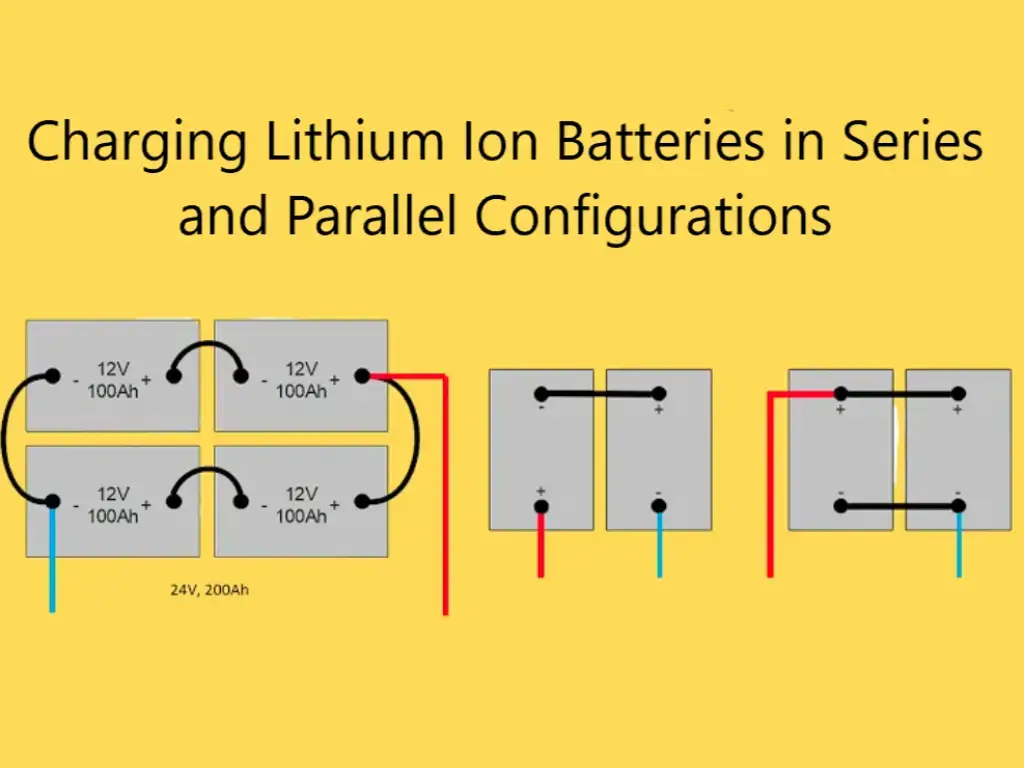
In this era of rapid technological development, the battery industry is an indispensable part of the current impact on the life of the most important batteries for lithium batteries and lead-acid batteries, but with the progress of science and technology, sodium-ion battery based on the unique advantages of the device and the potential for the development of the gradual emergence of people’s lives!
Follow us as we introduce you to the advantages and sustainability of sodium-ion batteries!

Basic Principles of Batteries
Sodium-ion batteries, lithium batteries and traditional lead-acid batteries are all chemical energy storage devices, but they all work differently. Here’s how each of these three batteries works:
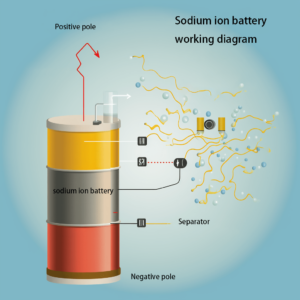
sodium-ion battery
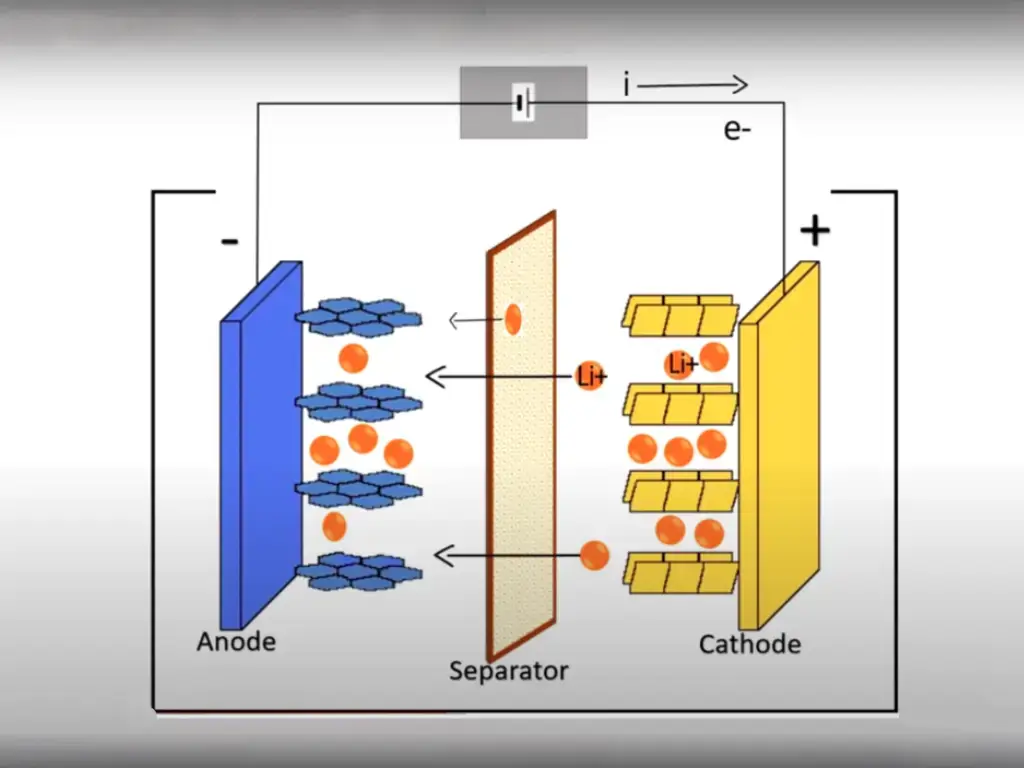
The working principle of sodium-ion battery is mainly the reversible operation of sodium ions between the motor materials.
In rechargeable battery sodium ions migrate from the positive electrode of the battery (usually a composite material containing sodium) through the electrolyte to the negative electrode (e.g. a carbon material) where they become embedded. This process is accompanied by the flow of electrons from the positive terminal to the negative terminal through an external circuit. When discharged, the sodium ions then migrate from the negative electrode back to the positive electrode, and the electrons flow in the opposite direction through the external circuit, resulting in the output of electrical energy.
The advantage of this battery system is its use of abundant and low-cost sodium.
lithium battery
Lithium battery technology focuses on the migration of lithium ions between graphite and lithium metal oxides at the positive and negative electrodes.
Lithium batteries are widely used in modern electronic devices due to their high energy density, long cycle life and low self-discharge rate.
lead-acid batteries
Lead-acid batteries are mainly a chemical reaction between lead and lead dioxide to produce electricity.
The main advantages of lead-acid batteries are their lower cost and technological maturity, but they have a lower energy density and are less environmentally friendly than lithium and sodium-ion batteries.
What materials are used in sodium-ion batteries?
Sodium ion batteries are mainly made of NaMnO2/ Na3V2(PO4)2F3/ Na2FeFe(CN)6/ Na2Fe2(SO4)3 they have different advantages before respectively!
NaMnO2
- Operating voltage: 3.2V.
- Operating temperature: -40°C to 80°C.
- Cycle life: ≥4500 cycles @ 83% (2C/2C).
- Energy density: ≥145Wh/kg.
- Multiplier performance: 5C capacity ≥90% of 1C capacity.
- Storage performance: 28 days storage at room temperature, charge retention rate ≥94% of rated capacity, charge recovery rate ≥99% of rated capacity.
Na3V2(PO4)2F3
- Operating voltage: 3.4V.
- Operating temperature: -20°C to 60°C.
- Cycle life: ≥3000 cycles @ 80% (1C/1C).
- Energy density: ≥120Wh/kg.
- Multiplier performance: 3C capacity ≥85% of 1C capacity.
- Storage performance: room temperature storage for 30 days, charge retention rate ≥ 90% of rated capacity, charge recovery rate ≥ 95% of rated capacity.
Na2FeFe(CN)6
- Operating voltage: 2.8V.
- Operating temperature: -10℃ to 50.
- Cycle life: ≥2000 cycles @75% (1C/1C).
- Energy density: ≥100Wh/kg.
- Multiplier performance: 2C capacity ≥80% of 1C capacity.
- Storage performance: 60 days storage at room temperature, charge retention rate ≥85% of rated capacity, charge recovery rate ≥90% of rated capacity.
Na2Fe2(SO4)3
- Operating voltage: 3.1V.
- Operating temperature: -30°C to 70°C.
- Cycle life: ≥3500 cycles @ 80% (1C/1C).
- Energy density: ≥130Wh/kg.
- Multiplier performance: 4C capacity ≥88% of 1C capacity.
- Storage performance: 45 days storage at room temperature, charge retention rate ≥ 92% of rated capacity, charge recovery rate ≥ 96% of rated capacity.
Advantages of sodium-ion batteries
- Cost advantage: Sodium ion is a higher raw material than lithium and is simpler in the manufacturing process, so it is lower in cost than lithium batteries
- Energy density: sodium ion energy density is lower than lithium batteries, but it is higher than the density of lead-acid batteries
- Safety: The sodium ion structure is stable, less danger of thermal runaway, and the safety risk after physical damage is less than lithium battery.
- Lifespan: the cycle life of sodium ion is higher than that of lead-acid battery and its service life is higher than that of lead-acid battery.
- Environmental impact: sodium ion is easier to decompose than lead-acid and lithium batteries when recycled.
- Price: Price is 10% higher than lead-acid batteries.
Sodium-ion batteries vs. lithium batteries vs. lead-acid battery.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Sodium-Ion Battery
Environmentally friendly.
Better safety.
Suitable for large-scale energy storage.
Lower technological maturity.
Limited market penetration.
Lithium battery
Low self-discharge rate.
High energy density.
Environmental impact.
Lead-acid batteries
Mature technology.
High power output.
High self-discharge rate.
High environmental pollution.
Maintenance requirement.
Barriers to Current Technical Problems of Sodium Ion battery.
- Energy Density: Sodium-ion batteries have a lower energy density compared to lithium-ion batteries. The larger atomic mass of sodium ions results in less energy being stored per unit volume or weight.
- Cycle stability: The cycle life and stability of sodium-ion batteries have not yet reached the same level as lithium-ion batteries. Especially under rapid charging and discharging and high temperatures, the performance of the battery degrades more significantly.
- Optimization of electrode materials: Currently, the positive electrode materials of sodium-ion batteries are usually transition metal oxides, while the negative electrode materials are mainly hard carbon. The performance and cost of these materials directly affect the overall performance of the battery.
- Electrolyte Improvement: Currently used liquid electrolytes may have safety concerns such as flammability and corrosiveness.
- Temperature sensitivity: The performance of sodium-ion batteries may not be as stable as lithium-ion batteries under extreme temperature conditions. Especially at low temperatures, the charging and discharging efficiency and capacity of the battery may drop significantly.
- Large-scale production and application: Sodium-ion battery technology still lags relatively behind in commercialization and large-scale application. Further research and development is needed to reduce production costs, improve manufacturing efficiency, and demonstrate its reliability and economic benefits in a variety of application scenarios.