A Brief Overview of LFP Batteries

Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries have emerged as a promising energy storage solution in various industries, ranging from electric vehicles to renewable energy systems. These batteries utilize lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material, offering advantages over traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Known for their stability and safety, LFP batteries are gaining popularity due to their long lifespan and high energy density. Unlike other lithium-ion variants, LFP batteries are less prone to thermal runaway and overheating issues, making them a reliable choice for critical applications where safety is paramount.
One of the key characteristics of LFP batteries is their ability to store a significant amount of energy in a compact space. This high energy density makes them ideal for electric vehicles seeking longer driving ranges and renewable energy storage systems aiming for efficient power generation and distribution.
The unique composition of lithium iron phosphate allows these batteries to maintain stable performance over an extended period, reducing the frequency of replacements and overall maintenance costs. As technology advances, LFP batteries continue to evolve, offering enhanced features that cater to the diverse needs of modern energy consumption.
The Importance Pros and Cons of LFP batteries
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, having a comprehensive understanding of the advantages and limitations of different battery technologies is crucial for informed decision-making. When it comes to selecting an appropriate power source for specific applications, weighing the pros and cons of LFP batteries becomes imperative.
By evaluating factors such as energy density, lifespan, safety features, maintenance requirements, specific power capabilities, initial costs, and temperature range limitations associated with LFP batteries, stakeholders can make informed choices that align with their goals and requirements. Furthermore, recognizing the significance of understanding these nuances empowers individuals and industries to optimize efficiency while ensuring sustainability in their operations.
Whether it’s transitioning towards greener transportation solutions or implementing robust energy storage systems for grid stability, being well-versed in the pros and cons of LFP batteries enables strategic planning and seamless integration into existing infrastructures. As we delve deeper into this exploration of battery technology advancements, unraveling the intricacies surrounding LFP batteries unveils a realm of possibilities that hold promise in shaping our future energy landscape.
The Pros of LFP Batteries
- Long Life: The durability and long life provided by LFP technology allow batteries to last much longer before needing replacement or maintenance. This extended life not only reduces long-term operating costs but also minimizes waste associated with frequent battery replacements, thereby increasing sustainability.
- High safety: especially about thermal runaway and overheating. This makes them the first choice for safety-critical applications such as electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
- Good thermal stability: Less susceptible to thermal runaway and other temperature-related problems. This makes them suitable for use in harsh environmental conditions.
- Fast charging: A convenient choice for applications that require fast and efficient charging, such as portable electronics and electric vehicles.
- Cost-effective: reduces the need for frequent battery replacements, and in the long term even though LFP batteries have a high initial cost, they have a long service life and are replaced less frequently.
- Low environmental impact: This is mainly because LFP batteries have a longer lifespan compared to other types of batteries. This means that over time, fewer batteries need to be manufactured and disposed of, thus reducing the overall environmental impact of battery technology.
- High Discharge Current: Li-FePO4 batteries provide high discharge current, which is beneficial for electric vehicles, power tools, drones, and other high-performance devices.
- Easy Maintenance: Li-FePO4 batteries typically require less maintenance. This reduces the need for a BMS and regular maintenance tasks.
Cons of LFP batteries
- Higher initial cost: The materials and manufacturing processes involved in producing LFP batteries result in a relatively high price point for these batteries. However, LFP batteries can still offer compelling economic benefits in the long run.
- Limited Temperature Range: Performance can be severely affected at extreme temperatures. Operating outside of optimal temperature conditions results in lower efficiency and reduced capacity of LFP batteries and may affect their safety characteristics. Current research is focused on improving the thermal stability of LFP battery designs. By enhancing heat dissipation mechanisms and optimizing internal structures, manufacturers hope to broaden the operating temperature range of these batteries while maintaining their core benefits of battery safety and long life.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points Regarding the Pros and Cons of LFP Batteries
In evaluating the pros and cons of Lithium batteries, it is evident that they offer a promising blend of advantages and disadvantages. On the positive side, LFP batteries boast high energy density, extended lifespan, enhanced safety features, and low maintenance requirements.
These qualities make them a compelling choice for applications requiring reliable long-term energy storage solutions. However, it is important to acknowledge the limitations such as lower specific power, higher initial cost, and limited temperature range that may influence their suitability for certain uses.
Importance of Considering These Factors When Choosing a Battery Technology
When selecting a battery technology for diverse applications ranging from electric vehicles to renewable energy storage systems, weighing the pros and cons of different options is paramount.
The decision-making process must involve careful consideration of factors like energy density requirements, operational lifespan expectations, safety considerations, maintenance costs, power delivery demands, initial investment outlay, and environmental conditions in which the batteries will operate. By meticulously assessing these aspects in light of specific project needs and sustainability goals, stakeholders can make informed choices that align with their objectives.

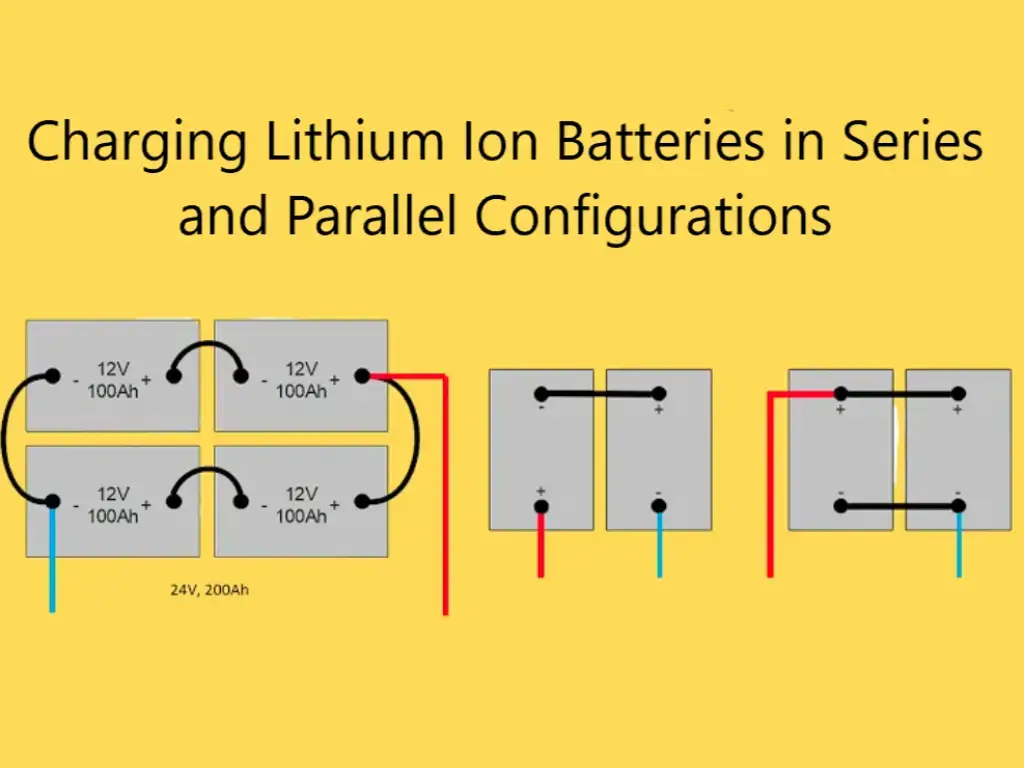

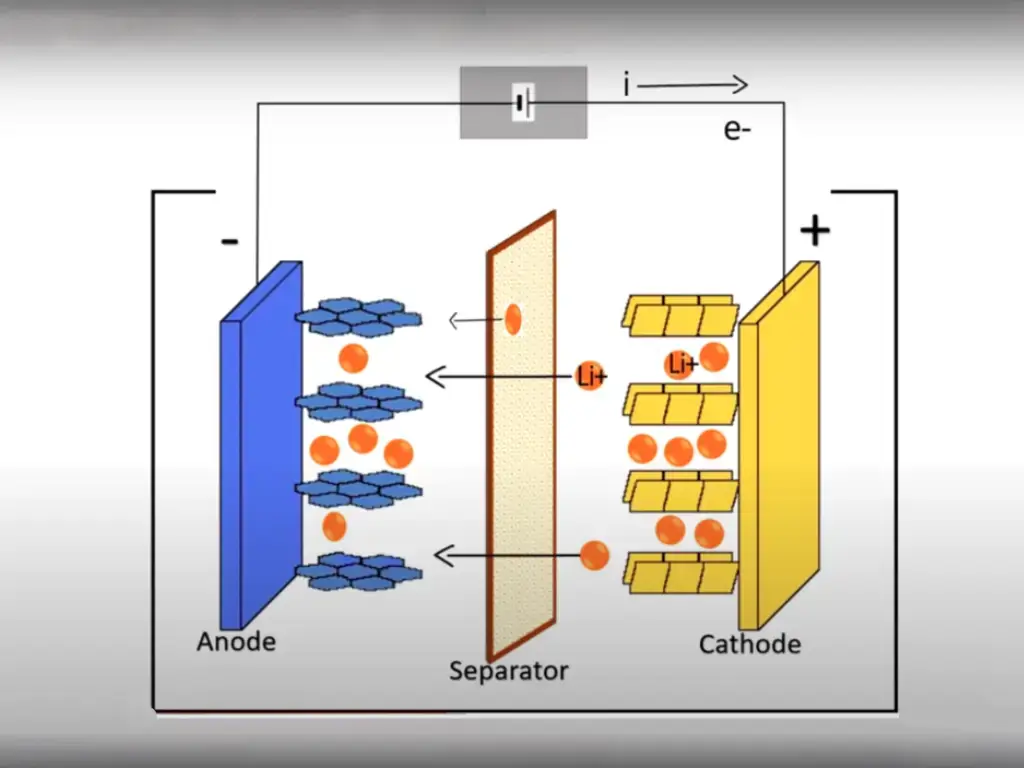

2 thoughts on “Unlocking the Potential: Understanding the Pros and Cons of LFP Batteries”
There are several pieces of misinformation here. LFP batteries do NOT have higher energy density than current NMC batteries. And they are cheaper, not more expensive. It’s very disappointing that a site called lithium battery tech.com can’t even get the basics right.
Hi Jarko
First of all I need to tell you that this blog just explains the advantages and disadvantages of LFP batteries and does not mention the comparison with NMC batteries.
Of course I know NMC energy density is bigger than LFP, and NMC price is bigger than LFP battery. But based on lead acid batteries the LFP is really expensive, even if it is not as expensive as NMC batteries!
Thanks for your feedback, we will try our best to do a better job with each blog!
Have a nice day!
CT