A Powerhouse Of Energy: Lithium Batteries In Modern Technology

Lithium batteries have become the powerhouse of energy storage in modern technology, powering a vast array of electronic devices from smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and renewable energy systems. Their lightweight design, high energy density, and long-lasting performance have made them the go-to choice for portable electronics and beyond. The use of lithium batteries has revolutionized industries by providing efficient and reliable power sources that enable our fast-paced, connected world to function seamlessly.
Unraveling The Mysteries: Understanding Lithium Battery Explosions
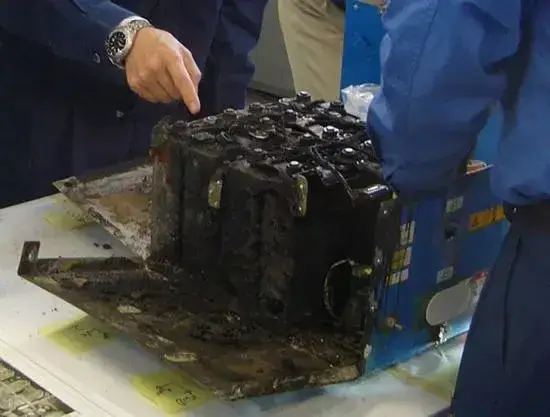

While lithium batteries offer numerous benefits, they also pose potential risks, most notably the risk of explosion. Understanding the causes behind lithium battery explosions is crucial for ensuring the safety of users and preventing catastrophic incidents.
These explosions can result from various factors such as overcharging, physical damage, manufacturing defects, or exposure to extreme temperatures. By delving into these causes and their mechanisms, we can implement strategies to mitigate risks and enhance safety measures in utilizing lithium batteries.
Importance Of Investigating Lithium Battery Explosions
The investigation into lithium battery explosions serves a critical purpose in safeguarding lives and property. Each incident provides valuable insights into the vulnerabilities of lithium batteries under different circumstances, guiding researchers and manufacturers towards developing safer battery technologies.
By unraveling the mysteries behind these explosions through thorough analysis and research, we pave the way for advancements that prioritize user safety without compromising on performance or efficiency. It is through this understanding that we can harness the full potential of lithium batteries while minimizing risks for a secure technological landscape.
Overcharge
Overcharging of lithium batteries is a common cause of explosions due to the buildup of unstable lithium metal deposits on the anode. When a battery is overcharged, it leads to an excessive flow of current, causing lithium ions to plate onto the anode in a non-uniform manner.
This uneven deposition creates dendrites or needle-like structures that can pierce the separator between the electrodes, leading to internal short circuits. The risk of thermal runaway and explosion further escalates as these dendrites continue to grow with subsequent charge cycles.
As more lithium metal accumulates, it increases the chances of direct contact between the anode and cathode, causing a rapid increase in temperature within the battery due to uncontrolled chemical reactions. This thermal runaway scenario can result in a violent release of energy and gases, ultimately culminating in an explosion.
Physical Damage
Physical damage remains another significant culprit behind lithium battery explosions. Impact or puncture on a battery can lead to internal short circuits within its structure. When the battery casing is compromised, it exposes reactive components such as the electrolytes to air or other materials present in its surroundings.
This exposure can trigger chemical reactions that release flammable gases and heat rapidly within the confined space of the battery cell. The build-up of pressure from these reactions can cause the battery casing to rupture explosively, releasing potentially hazardous materials and leading to a sudden explosion.
Manufacturing Defects
Poorly designed or faulty batteries resulting from manufacturing defects pose a serious threat as they are prone to internal shorts or overheating. Issues such as substandard materials used in construction or improper assembly processes can compromise the integrity and safety mechanisms within a lithium battery.
Lack of stringent quality control measures during production further exacerbates these risks by allowing defective batteries with hidden flaws to enter circulation undetected. Without proper safeguards in place, such batteries may exhibit erratic behavior under normal usage conditions, increasing the likelihood of critical failures that could lead to catastrophic outcomes like explosions.
Over-Discharge
Battery over-discharge or over-current discharge (more than 3C) is easy to make the negative electrode copper foil dissolved and deposited on the diaphragm so that the positive and negative electrodes are directly short-circuited to produce an explosion (rarely occurs). Lithium battery cells should also have a lower voltage limit when discharging. When the voltage of the battery cell is lower than 2.4V, some materials will begin to be destroyed. And because the battery will self-discharge, the longer you put the lower the voltage will be, therefore, it is best not to discharge to 2.4V before stopping. Lithium batteries from 3.0V to 2.4V discharge period, the energy released only accounts for about 3% of the battery capacity. Therefore, 3.0V is an ideal cut-off voltage for discharge.
Overcurrent
Protection line out of control or detection cabinet out of control so that the charging current is too large to cause lithium ions to be embedded in time, but the formation of lithium metal on the surface of the pole piece, penetrating the diaphragm, positive and negative electrode direct short circuit resulting in an explosion (seldom occurs). Charge and discharge, in addition to the voltage limit, the current limit is also necessary. When the current is too high, lithium ions will not have time to enter the storage compartment and will gather on the surface of the material.
Battery Aging
As batteries are used over time, their internal chemistry may change, increasing the risk of explosion.
Excessive Moisture Content
Moisture can react with the electrolyte in the lithium battery cell to produce gas, when charging, it can react with the generated lithium to produce lithium oxide, making the capacity loss of the battery cell, easy to overcharge the battery cell and generate gas, the decomposition voltage of the water is low, it is easy to decompose and generate gas when charging, when this series of generated gases will make the battery cell’s internal pressure increase, and when the battery cell’s casing can’t withstand it, lithium batteries will explode.
If The Causes Of Battery Explosions Are Analyzed More Closely, There Are Also The Following Scenarios
- Greater internal polarization.
- The pole piece absorbs water and reacts with the electrolyte gas drum.
- The quality and performance of the electrolyte itself.
- Liquid injection when the liquid injection amount does not meet the process requirements.
- Poor sealing performance of laser welding in the assembly process, and air leakage when measuring air leakage.
- Dust, pole piece dust is easy to cause micro-short circuits in the first place.
- Positive and negative pole pieces are thicker than the process range, and it is difficult to enter the shell.
- Liquid injection sealing problem, steel ball sealing performance is not good leading to air drum.
- Shell incoming materials exist in shell wall thickness, shell deformation affects the thickness.
- High outside ambient temperature is also the main cause of the explosion.
Charging Safely: A Crucial Step Towards Battery Safety
When it comes to lithium batteries, proper charging practices are paramount in preventing potential explosions. Using chargers specifically designed for lithium batteries, equipped with built-in safety features such as overcharge protection and temperature monitoring, is essential. These chargers are engineered to deliver the correct voltage and current levels, safeguarding against overcharging that can lead to thermal runaway and ultimately, an explosion.
Avoid the temptation of leaving your devices plugged in overnight or resorting to cheap, unregulated chargers that lack the necessary safety mechanisms. Remember, investing in a quality charger is an investment in the longevity and safety of your devices.
Common Types Of Explosions:
Explosions Caused By Thermal Shock:
A battery explosion is due to the decomposition of the solvent, the decomposition of the cathode material, and the cathode material and electrolyte reaction generates a large amount of heat and gas.
Explosion Caused By Overcharging:
The use of a damaged or non-specialized charger to charge the battery may cause the battery fast charging. Lithium-ion battery overcharge voltage-temperature pattern has three forms:
① When the charging voltage exceeds 4.5V, a large number of lithium ions overflow from the positive electrode, if the negative electrode of the embedded lithium is very poor, lithium ions will be deposited on the surface of the negative electrode to form dendrites, that the battery internal short-circuit, the battery’s safety is significantly reduced;
② If the negative electrode of the embedded lithium is relatively strong, with the lithium ions overflowing from the positive electrode, the solvent is oxidized (much greater than the If the lithium embedded capacity of the negative electrode is relatively strong, as lithium ions overflow from the positive electrode, the solvent is oxidized (much greater than the rate of the normal reaction), generating a large amount of heat to raise the temperature of the battery, followed by the reaction of the solvent and the negative electrode occurs at the same time, releasing more heat. If the charging current is very low, the thermal stability of the battery is good, the rate of heat generation is balanced with the rate of heat dissipation, the products of electrolyte decomposition increase the internal resistance of the battery, or the diaphragm is closed, the voltage rises first, and then remain constant, the heat will not get out of control.
③ If the charging current is very large (2C), the stability of the battery is still very poor, the voltage and the temperature rise rapidly, and the battery will catch fire and explode.
Explosion Caused By Short Circuit:
Explosion caused by short circuit: The contact between positive and negative lugs of the battery may cause an external short circuit of the battery; Collector burrs, diaphragm wrinkles, and poor assembly during the assembly process can trigger an internal short circuit, and the short circuit may also cause the battery to explode.
Handling And Storage Guidelines
Proper handling and storage of lithium batteries play a crucial role in mitigating explosion risks. Store your batteries in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight or heat sources to maintain optimal operating conditions. Extreme temperatures can compromise battery integrity and increase the likelihood of thermal runaway.
Furthermore, protect your batteries from physical damage by utilizing protective cases or sleeves when transporting them. A minor impact or puncture can potentially lead to internal short circuits within the battery, paving the way for catastrophic consequences.
Quality Assurance And Inspection
Ensuring that lithium battery products meet industry standards is a cornerstone of preventing explosions due to manufacturing defects. Quality assurance measures should include rigorous testing procedures before products hit the market. Products that undergo comprehensive inspection are more likely to exhibit superior performance and reduced safety risks.
By prioritizing quality control throughout every stage of production, manufacturers can uphold excellence in delivering reliable lithium battery solutions that instill confidence in consumers.
Conclusion:
As we navigate the intricate realm of lithium battery safety, it becomes evident that knowledge combined with conscientious practices plays a pivotal role in averting potential disasters.
By adhering to proper charging protocols, handling guidelines, quality assurance measures, and promoting education on safe practices among users, we collectively contribute towards creating a safer environment for utilizing lithium batteries with peace of mind. Let us embrace these preventive measures not as restrictions but as empowering tools that enable us to harness cutting-edge technology responsibly while ensuring our well-being.



1 thought on “Unveiling Lithium Battery Explosions: Deciphering Dangers”
interesting discussion. commenting to be on mail list