Introduction
In this technology-driven world, it is imperative to realize the battery technology. This is true for the battery reserve capacity concept which is used often while talking about cars, boats, or off-grid energy solutions. On the other hand, not everyone understand the real essence of it. This guide will help you to clarify any questions you might have. It will define battery reserve capacity, describe the way it is measured, and highlight the importance of it for your devices and vehicles. We will delve into the specifics to paint a more complete picture. This way, you can make smart choices about your batteries.

What is Reserve Capacity on a Battery?
Reserve capacity (RC), also called reserve minutes, is a great indicator of battery performance which is equal to the length of time in which the battery can supply power to the critical systems under specified conditions without charging. In order to evaluate that, there is a standard test. The fully charged battery is operated at a warm temperature (80°F) until it can’t deliver the desired amount of power (25 amps). When the voltage is 10.5 volts, the test is over. And the number of minutes is battery reserve capapcity. The Battery Council International (BCI) is the administrator of this test and all companies are required to follow the same procedure. This implies that you can make like for like comparison of different batteries to know the one that lasts longer. A battery with a higher reserve capacity will be more reliable and will be able to keep your vehicle or device functioning longer even when there is a power outage. This indicator is crucial under the circumstances where reliability is not an option-for example, emergency medical systems, automotive reliability, and the off-grid energy storage solutions.
Cold cranking amps (CCA) on the other hand are not the same as reserve capacity. CCA means how well a battery can start an engine in cold temperatures. While CCA is crucial for starting an engine, reserve capacity is about the power staying on for longer.
Why Does Battery Reserve Capacity Matter?
Reserve capacity is important for several reasons. First, it shows how well a battery can handle consistent loads (not short bursts). This is vital for systems that need reliable power. Second, it gives us a clue about the battery’s health and life span. A battery losing reserve capacity might be close to the end of its life. Third, for people working in automotive, marine, or renewable energy, understanding reserve capacity helps improve battery storage. It ensures batteries can meet power needs now and keep running without power for longer.
The importance of reserve capacity is growing with new battery technologies. For example, thin plate pure lead (TPPL) and lithium-ion batteries are changing the game. They store more energy and release it more efficiently. These changes are pushing the limits of what batteries can do. For experts in the battery field, keeping up with these changes is key. They greatly affect how batteries are chosen and used in different settings.
Comparing Reserve Capacity and Amp Hours
Even though the reserve capacity and amp hours (Ah) both express battery’s energy-storing capacity, they depict different aspects of battery performance. Amp hours signify the total electrical energy a battery has the capacity to store, while reserve capacity quantifies the specific amount of time a battery can maintain a constant load before it is drained.
To better understand the difference, consider this example: A battery with a 100 Ah capacity, 100-minute reserve capacity, and 10.5-volt voltage drop can deliver 25 amps for 100 minutes until the battery voltage drops below 10.5 volts. On the other hand, the same battery would be capable of delivering 50 amps for a shorter period or 10 amps for a longer period. The amp-hour rating is the total energy capacity, and reserve capacity is the indication of how long the battery can sustain a particular load.
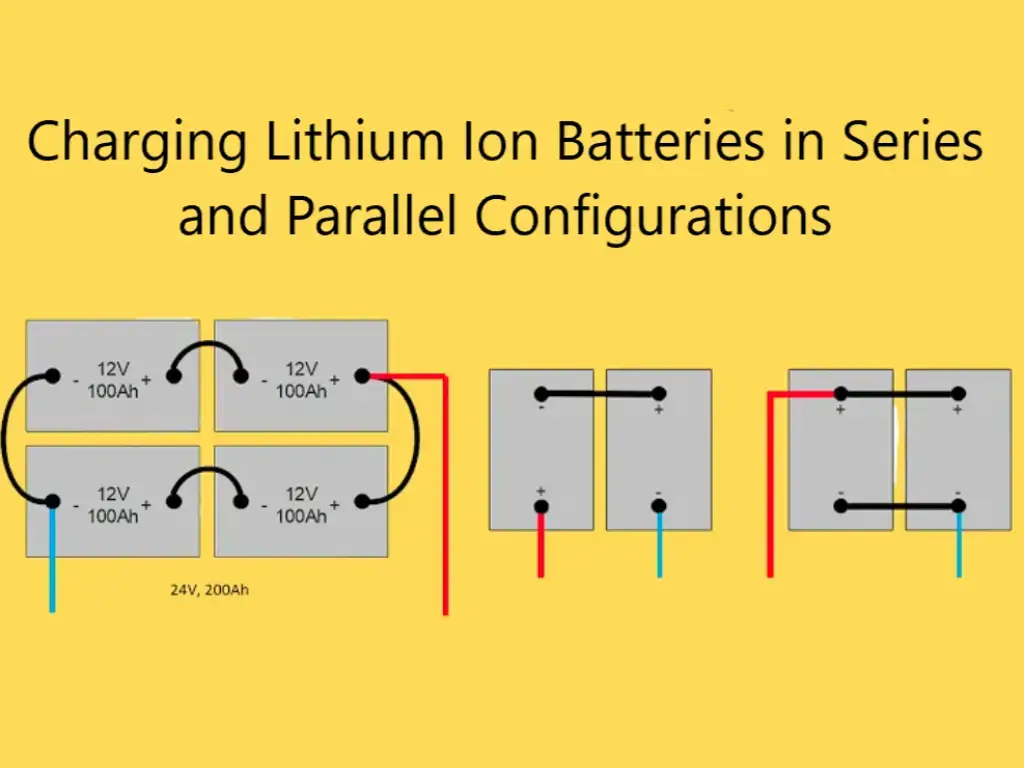
The term reserve capacity is more often used in the context of lead-acid batteries and it directly measures the endurance and reliability in cases such as automotive and marine applications where safeguarding power for the vital functions in case of a failure is critical. Lithium batteries, which have high energy density and are able to withstand a deeper discharge cycle, also have a reserve capacity that could be calculated theoretically. But, manufacturers of the lithium battery do not usually disclose the reserve capacity data, they only highlight the amp-hour rating as it is more versatile across different applications from small electronics to electric vehicles.
How to Calculate Battery Reserve Capacity?
To calculate a battery’s reserve capacity rating, you’ll need to know its amp-hour rating and the desired discharge current. Use the following formula:
Reserve Capacity (minutes) = (Amp-Hours × 60) ÷ Discharge Current (amps)
For example, if you have a 100 Ah battery and want to know its reserve capacity at a 25-amp discharge rate:
Reserve Capacity = (100 Ah × 60) ÷ 25 amps = 6000 ÷ 25 = 240 minutes
Keep in mind that this calculation provides an estimate based on ideal conditions. Factors such as temperature, battery age, and discharge rate can affect the actual reserve capacity.
Types of Batteries and Their Reserve Capacities
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead acid batteries are widely used in vehicles and other areas. They are reliable and affordable. Plus, they usually have high reserve capacities. There are different kinds of lead-acid batteries. These include flooded (wet cell), sealed maintenance-free (SMF), and absorbent glass mat (AGM) batteries.
Flooded lead-acid batteries often have the highest reserve capacities in this group. But, they need regular checks and maintenance. You have to keep an eye on the electrolyte levels and add distilled water when needed. On the other hand, SMF batteries don’t need this upkeep. They have a lower reserve capacity than flooded batteries. AGM batteries use a glass mat to hold the electrolyte. They have high reserve capacities too. Plus, they are better at handling shakes and extreme temperatures.
However, it’s crucial to approach the notion of tapping into a lead-acid battery’s full reserve capacity with caution. Pushing a battery to its reserve limit can plummet its voltage to 10.5 volts, dipping well below half its charge capacity. Such deep discharges pose a significant threat to the battery’s overall health and can drastically reduce its lifespan. Hence, it’s wise to view a battery’s reserve capacity more as a safety margin rather than a regular operational benchmark, steering clear of deep discharges that can prematurely end a battery’s life.
Related Post: What is Depth of Discharge? Everything You Need to Know

Lithium Batteries
Lithium batteries, especially lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) types, are becoming more popular. They are light, have lots of energy for their size, and last a long time. They also have great reserve capacities, often better than lead-acid batteries. This is because lead-acid batteries exhibit the Peukert effect, a phenomenon where their available capacity decreases as the rate of discharge increases. This means that at higher power demands, lead-acid batteries can’t deliver their full rated capacity, reducing their efficiency in power-intensive applications. But, lithium batteries cost more. They might also need special charging equipment.
The ampere-hour rating of lithium batteries more accurately reflects the actual amount of energy you can expect to receive under most conditions. These batteries fit well in situations that need lots of power drains, like solar power storage or electric cars. They’re also good for vehicles that use a lot of power or go off-grid often.
Nickel-Cadmium and Other Types
Nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries are tough and work well in hot or cold weather. They have solid reserve capacities and can be used a lot without losing much power. But, NiCd batteries cost more than lead-acid types. They can also suffer from the “memory effect.” This means they might hold less charge over time if they’re not fully used before charging again.
There are also other batteries like nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) and nickel-zinc (NiZn). Their reserve capacities vary based on their chemistry and design. These types are not as common in cars. But, they are used in some industries and gadgets.
How Temperature Affects Reserve Capacity
Temperature has a big impact on a battery’s reserve capacity. When it gets colder, the chemical reactions inside the battery slow down. This makes the battery less able to produce current. So, in cold weather, a battery won’t have as much reserve capacity as it does at 80°F (27°C).
To help with this, battery makers often list reserve capacities for different temperatures, like 32°F (0°C) or even 0°F (-18°C). If you’re picking a battery for a place with cold winters, you should look at the reserve capacity for the coldest temperature you expect. This way, you can make sure the battery will work well, even when it’s really cold.
On the flip side, high temperatures can hurt a battery’s reserve capacity too. Hot weather speeds up the battery’s chemical reactions. This can make the battery lose its charge faster and shorten its life. To deal with high heat, it’s important to take good care of your battery. Keep it charged correctly and store it in a place that’s cool and dry when you’re not using it. This helps your battery stay in good shape, no matter the temperature.

Choosing the Right Battery Based on Reserve Capacity
When selecting a battery based on its reserve capacity, consider the following factors:
| Electrical demands | Determine the electrical loads your vehicle or device will place on the battery, including accessories like windshield wipers, lights, and audio systems. |
| Climate | Consider the temperature range in which you’ll be using the battery. If you live in a cold climate, choose a battery with a higher reserve capacity at low temperatures. |
| Usage patterns | Think about how you’ll be using the battery. If you frequently use your vehicle for short trips or have a tendency to leave accessories running while the engine is off, opt for a battery with a higher reserve capacity. |
| Space constraints | Make sure the battery you choose fits your vehicle’s battery compartment and meets any size or weight restrictions. |
| Budget | Balance your performance needs with your budget. Higher reserve capacity batteries may be more expensive, but they can provide added peace of mind and longer service life. |
Extending Battery Life and Reserve Capacity
To enhance the life and reserve power of your battery, here are some essential tips to follow:
- Keep your battery clean and dry: It’s important to regularly wipe down the battery terminals and connections to avoid corrosion. Corrosion can lead to decreased performance and a shorter lifespan for your battery.
- Check and maintain electrolyte levels: For those with a traditional lead-acid battery, it’s crucial to keep an eye on the electrolyte levels and refill with distilled water as necessary.
- Avoid letting your battery run low: Make sure to recharge your battery frequently and try not to let it fall below half its capacity. Allowing your battery to run too low can significantly shorten its life.
- Choose the right charger: Using a charger that’s suited for your battery’s type and size is key. The wrong charger can cause overcharging or undercharging, damaging your battery.
- Store batteries correctly: If you’re not going to use your batteries for a while, store them in a cool, dry place and keep them charged to about 50-70% to reduce self-discharge and extend their lifespan.
Conclusion
The reserve capacity of a battery is an essential aspect to consider when picking a battery for your vehicle or device. This capacity indicates how long a battery can supply power without recharging, which is vital if the charging system breaks down or when using accessories without the engine running. By understanding reserve capacity, how it’s measured, and how different factors like temperature and the type of battery impact it, you can choose the most suitable battery for your needs.
When selecting a battery, keep in mind your vehicle’s power requirements, the climate, how you’ll use the vehicle, and your budget. Proper maintenance, such as cleaning, keeping an eye on electrolyte levels, and avoiding letting your battery’s charge get too low, will help increase the life of your battery and ensure it performs well when you need it the most.
Looking to power up your next adventure or ensure your vehicle is equipped with the best energy solution? Let our team guide you to the perfect battery choice, tailored to your unique needs. Whether it’s for marine adventures, off-grid living, or ensuring your car is ready for the road ahead, we’re here to help. Reach out to us today, and let’s embark on this journey to optimal power together.