Introduction

The Vital Role of Batteries in Modern Society
In our fast-paced, technology-driven world, batteries play a vital role in powering the various devices that simplify and improve our lives. From smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems, the need for efficient, reliable, and long-lasting battery solutions is growing every day. As society continues to embrace sustainable practices and shift to cleaner energy sources, the choice of battery technology becomes even more important.
Overview of Lithium Iron Phosphate, Lithium Ion and Lithium Polymer Batteries
Among the many battery options on the market today, three stand out: lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), lithium ion (Li-Ion) and lithium polymer (Li-Po). Each type of battery has unique characteristics that make it suitable for specific applications, with different trade-offs between performance metrics such as energy density, cycle life, safety and cost. By understanding the nuances of these battery chemistries, we can make informed decisions when selecting the most appropriate power source for a device or system.
Uncovering the Unique Characteristics of Lifepo4 VS. Li-Ion VS. Li-PO Battery
In a comprehensive comparison of Lifepo4 VS. Li-Ion VS. Li-PO Battery, we will unravel the intricate chemistry behind each. By exploring their composition at the molecular level and examining how these components interact with each other during charge/discharge cycles, we can understand the unique advantages and limitations of each technology. Through this exploration, we aim to shed light on which battery type may have supremacy in various situations based on specific criteria such as safety standards, life expectancy, energy density requirements, and environmental sustainability goals.
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Battery
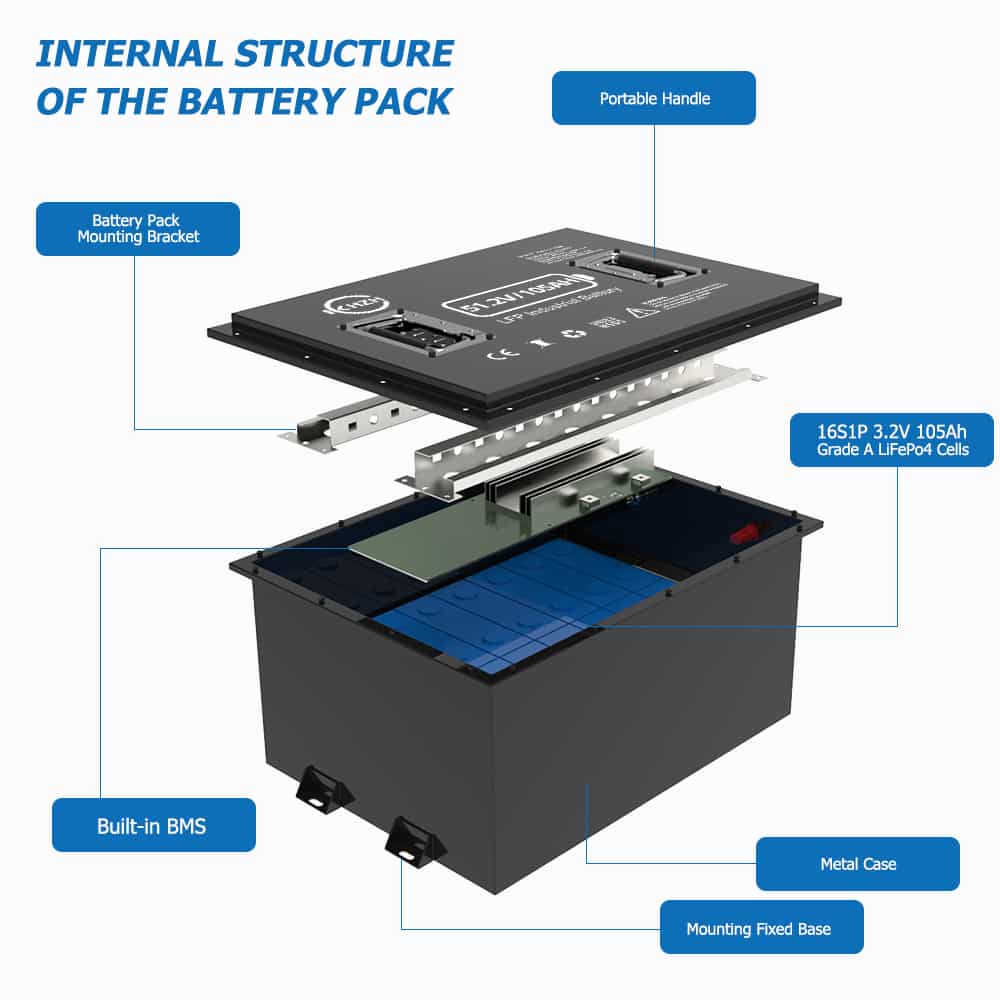
Chemistry and Structure

The LiFePO4 battery, also known as the lithium iron phosphate battery, consists of a cathode made of lithium iron phosphate, an anode typically composed of graphite, and an electrolyte that facilitates the flow of lithium ions between the two electrodes. The unique crystal structure of LiFePO4 allows for the stable release and uptake of lithium ions during charge and discharge cycles, contributing to its longevity and safety profile.

Composition of Cathode, Anode, and Electrolyte
The cathode in a LiFePO4 battery is primarily made up of lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), which is known for its high thermal stability and safety compared to other materials like cobalt oxide used in traditional lithium-ion batteries. The anode consists of graphite, a common choice due to its ability to intercalate lithium ions efficiently. The electrolyte used in LiFePO4 batteries is typically a non-flammable organic solvent or a polymer gel that allows for the movement of lithium ions without posing significant safety risks.
Unique Features that Distinguish it from Other Lithium-based Batteries
One key feature that sets LiFePO4 batteries apart from other lithium-based batteries is their exceptional thermal stability and safety profile. Unlike conventional lithium-ion batteries that may experience thermal runaway under certain conditions, LiFePO4 cells are much less prone to overheating or fire hazards. Additionally, LiFePO4 batteries exhibit a long cycle life with minimal capacity degradation over repeated charge-discharge cycles, making them ideal for applications requiring durability and reliability.
Pros And Cons
High Thermal Stability and Safety
The high thermal stability of LiFePO4 batteries is a significant advantage over other types of lithium-based batteries. This inherent property reduces the risk of thermal runaway events that can lead to battery fires or explosions. As such, LiFePO4 batteries are preferred for applications where safety is paramount, such as in Industrial Battery (Lithium Forklift Battery/ AGV Battery) or Energy Storage System (C&I ESS/ Marine ESS) where large battery packs are utilized.
Long Cycle Life
Another notable advantage of LiFePO4 batteries is their extended cycle life compared to traditional lithium-ion counterparts. Due to the robust crystal structure of lithium iron phosphate material, these batteries can endure thousands of charge-discharge cycles with minimal capacity fade. This longevity makes them cost-effective solutions for applications requiring reliable power sources over an extended period.
Environmental Friendliness
LiFePO4 batteries are considered more environmentally friendly than some other types of lithium-based batteries due to their composition without harmful heavy metals like cobalt or nickel found in conventional lithium-ion cells. This eco-friendly aspect makes them appealing choices for sustainable energy storage solutions where reducing carbon footprint and toxic waste generation are essential considerations.
Lower Energy Density Compared to Other Lithium-based Batteries
Despite their many advantages, one notable drawback of LiFePO4 batteries is their lower energy density compared to other types of lithium-based chemistries like nickel-cobalt-aluminum oxide (NCA) or nickel-manganese-cobalt oxide (NMC). This lower energy density translates into reduced specific energy levels per unit weight or volume, limiting the overall energy storage capacity achievable in devices powered by these cells.
Higher Cost
Another disadvantage associated with LiFePO4 batteries is their relatively higher manufacturing cost when compared to standard lithium-ion options utilizing cobalt or nickel chemistry. The production process for quality LiFePO4 cells involves sophisticated manufacturing techniques and materials that contribute to elevated costs per unit. While prices have been gradually decreasing as technology advances and economies of scale improve production efficiencies, initial investment outlay remains a consideration for some applications seeking cost-effective power solutions.
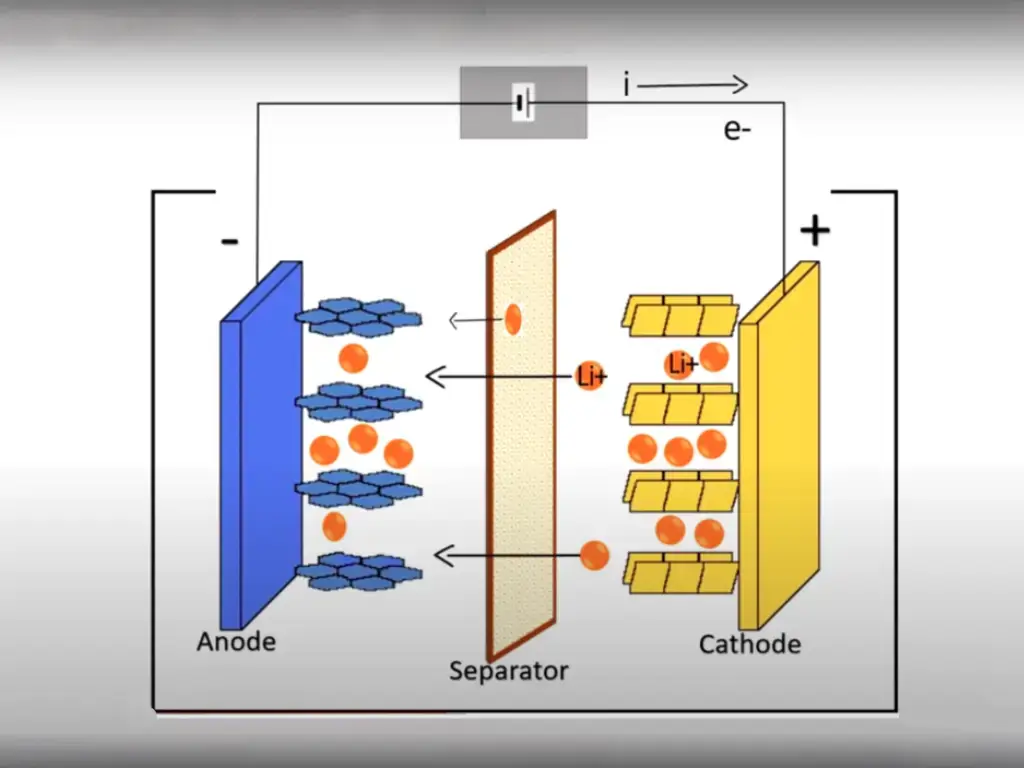
Exploring the Chemistry and Structure of Li-Ion Batteries
Within a lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery, the cathode typically consists of lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), while the anode is commonly made of graphite. The electrolyte is usually a lithium salt dissolved in a solvent, facilitating the movement of lithium ions between the cathode and anode during charging and discharging cycles. This unique composition allows for efficient energy transfer within the battery cell.
-
24V Lithium Battery
24v 60Ah Lithium Drop-ln Replacement Battery
-
24V Lithium Battery
24V 18650 Lithium Battery With Waterproof Case
-
24V Lithium Battery
24V 150Ah AGV/AMR Robot Lithium Battery
-
24V Lithium Battery
24v 50ah lithium iron phosphate battery
-
12V Lithium Batteries
Custom 12V 100ah Slim lithium battery for RVS
-
12V Lithium Batteries
12V Lithium Ion Battery Heater and Drop-In Replacement
The Major Characteristics Defining Li-Ion Battery Performance
One of the key defining features of Li-ion batteries is their high energy density, which refers to the amount of energy stored per unit volume or weight. This characteristic makes Li-ion batteries popular in various applications where space and weight are critical factors. Additionally, Li-ion batteries boast a wide range of applications, from powering smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Li-Ion Batteries
Li-ion batteries offer several advantages, including their high energy density that enables long-lasting power in compact sizes. Their versatility allows them to be used across a broad spectrum of devices and industries due to their reliable performance.
However, these batteries come with inherent risks such as overheating or potential explosion if not handled properly. Furthermore, over time, Li-ion batteries experience a gradual decrease in capacity as a result of chemical reactions within the battery cells.
Exploring the Chemistry and Structure of Lithium Polymer (Li-Po) Battery
Composition of Cathode, Anode, and Electrolyte:
The cathode of a Lithium Polymer (Li-Po) battery is typically made from a lithium cobalt oxide compound, while the anode consists of lithium mixed with various carbon-based materials. The electrolyte in Li-Po batteries is a polymer substance that effectively conducts lithium ions between the cathode and anode. Unlike traditional liquid electrolytes used in other lithium-based batteries, the polymer electrolyte in Li-Po batteries offers greater flexibility and design possibilities.
Distinctive Features Setting Li-Po Batteries Apart:
One of the key distinguishing features of Li-Po batteries is their lightweight design. This characteristic makes them ideal for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in drones or remote-controlled vehicles.
Additionally, Li-Po batteries boast a flexible form factor due to their use of polymer electrolytes, allowing for custom shapes and sizes to fit specific device requirements. This flexibility opens up new possibilities for innovative product designs in various industries.
The Advantages of Lithium Polymer (Li-Po) Batteries
Lightweight Design:
The lightweight nature of Li-Po batteries makes them highly desirable for portable electronics and applications where weight reduction is essential. Their high energy density relative to their weight makes them an efficient choice for devices that require long-lasting power without added bulk. From wearable technology to aerospace systems, the lightweight design of Li-Po batteries offers unparalleled performance in diverse settings.
Flexible Form Factor:
Another significant advantage of Li-Po batteries lies in their flexible form factor. Traditional rigid battery shapes can limit product design options, but with Li-Po technology’s flexibility, manufacturers can create sleeker and more ergonomic devices. This feature has revolutionized the way electronic gadgets are designed, enabling better integration into smaller spaces while maintaining optimal functionality.
The Pros of Lithium Polymer (Li-Po) Batteries
Sensitivity to Overcharging: Li-Po batteries can be quite sensitive to overcharging. Exceeding the recommended charge voltage, even slightly, can significantly increase the risk of overheating, swelling, and potentially causing a fire or explosion.
Swelling: One of the more common issues with Li-Po batteries is swelling or puffing up, which occurs due to gas build-up inside the battery when it’s overcharged, over-discharged, or exposed to excessive heat. This can compromise the battery’s performance and longevity, and in some cases, make it unsafe to use.
Require Careful Handling: Li-Po batteries require careful handling and storage. They must be stored in a fireproof container and charged in a safe area due to their risk of catching fire if damaged or improperly handled. They also should not be punctured or physically damaged.
Cost: Compared to other types of rechargeable batteries, such as Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH), Li-Po batteries can be more expensive to manufacture and purchase. This cost factor can be significant, especially for large-scale applications.
Complex Charging Circuitry: Li-Po batteries require precise control over the charging process, necessitating complex charging circuitry. This is to avoid overcharging and undercharging, both of which can significantly affect their lifespan and safety.
Limited Lifecycle: While Li-Po batteries have a relatively good number of charge/discharge cycles, they don’t last as long as some other types of batteries. Their performance begins to degrade after a certain number of cycles or a few years of use, whichever comes first.
Temperature Sensitivity: Their performance can be significantly impacted by extreme temperatures. They perform poorly in cold conditions and can be dangerous if used or charged in very hot conditions due to increased risk of thermal runaway.
Disposal and Environmental Concerns: Proper disposal of Li-Po batteries is crucial because they contain environmentally harmful materials. However, recycling options are limited compared to other types of batteries, posing potential environmental issues.
LiFePO4 VS. Li-ion VS. Li-Po Battery Conclusion
Despite each type of lithium-based battery having its unique characteristics and applications, it’s clear that Lifepo4 batteries stand out for their lightweight design and flexible form factor. These attributes make them particularly well-suited for modern technological demands where portability and customization are paramount concerns.
Embracing advancements in battery technology like LFP not only enhances device performance but also opens up opportunities for innovation across industries. Let’s look forward to a future powered by ever-evolving energy solutions that drive progress and efficiency forward!









4 thoughts on “LiFePO4 VS. Li-ion VS. Li-Po Battery Complete Guide”
The information given in this article is great. I would just love to visit your website again in search of unique and great content with many different topics
It takes the better part of 100kWh to move a good electric car 1/4 mile.
usable capacity in some instances is much less when cold, so a 1kWh pack might actually deliver 500Wh when frozen and just to get it to operating temp essentially drains it at an equivalent 2x rate.
Your words are like a symphony, each note harmonious and beautiful. Your article is a joy to read.