Investing in solar batteries for your home is a significant step towards self-sufficiency, reducing electricity bills, and promoting a sustainable, green lifestyle. With the increasing demand for renewable energy storage, the market is flooded with a variety of options, making the selection process daunting.
This buyer’s guide is crafted to navigate you through the various options of solar batteries, demystifying the technical jargon and presenting a streamlined approach to help you make an informed decision.
We delve into the core aspects, ensuring that you select a solar battery that not only meets your energy needs but is also aligned with your budget and environmental values.
What are Solar Batteries?
Solar batteries, better known as solar energy storage battery systems are specialized storage devices designed to retain excess energy produced by your solar panels. Unlike traditional batteries, these are optimized to work seamlessly with the unique demands and fluctuations of solar energy systems.
In essence, during times when your solar panels are producing more electricity than your home is consuming, instead of sending this excess power back to the grid (or wasting it entirely), a solar battery will store it. Then, during periods when the sun isn’t shining—like at nighttime or on cloudy days—your home can tap into this stored energy, ensuring a consistent power supply.

What Are The Types of Solar Batteries?
here are various types of solar energy storage batteries in the market, including:
● Lead-Acid Batteries:
The oldest type of rechargeable battery, lead-acid batteries are often the most economical choice but tend to have a shorter lifespan and lower energy density.
● Lithium-ion batteries: These have gained immense popularity in recent years due to their longer lifespan, higher efficiency, and decreasing costs. They’re commonly found in many modern electronics, including smartphones and electric vehicles.
● Saltwater Batteries:
An emerging option is that saltwater batteries use saltwater electrolytes to store energy. They are more environmentally friendly than other options and do not contain heavy metals.
● Flow Batteries: These batteries use two chemical components dissolved in liquids to capture and store energy. They’re known for their long duration and ability to be discharged fully without harm.
Understanding the fundamental concepts and types of solar batteries is the first step in evaluating which one is the right fit for your home. In subsequent sections, we will dive deeper into the specifications and factors to consider when selecting the best solar battery for your needs.
Essential Points To Consider When Choosing A Solar Battery Storage System
1- Capacity & Power:
Capacity refers to the total amount of electricity that a battery can store, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). It’s crucial to determine how much energy your home typically consumes in a day to select a battery with the right capacity.
There are two different types of capacity rating:
- Total capacity
- Usable capacity
You have to focus on the second one- the usable capacity. So, how much battery capacity is recommended?
You need a solar home battery storage system with a storage capacity rating of at least 10kWh. Yes! If you have high usage in the evening, you must opt for a higher capacity rating to ensure you have enough energy stored.
Power pertains to the amount of electricity a battery can deliver at one time, measured in kilowatts (kW). It dictates how many appliances or devices you can run simultaneously using the stored energy.
Like capacity ratings, there are two types of power ratings:
- Continuous power rating
- Peak power rating
Continuous Power Rating refers to the maximum amount of power the battery can consistently deliver over an extended period. Peak power rating denotes the maximum power the battery can provide in short bursts, typically for situations where there’s a sudden high demand.
Mostly, you get solar batteries with a Continuous power rating (5kW) and Peak power rating (7kW), which is also the recommended power rating.
NOTE: Choosing a battery isn’t just about getting the one with the highest capacity or power. It’s about balancing the two. A battery might have a high capacity (stores a lot of energy) but a low power rating (delivers that energy slowly). Conversely, another might deliver a lot of power but drain quickly due to a lower capacity. The right balance depends on individual household needs.
2- Depth of Discharge (DoD):
Most batteries need to retain a certain percentage of their charge and cannot be fully depleted. DoD represents the amount of battery capacity that is usable.
For instance, a 10 kWh battery with a 90% DoD provides 9 kWh of usable storage. It’s preferable to opt for batteries with a higher DoD.
3- Lifespan & Warranty:
The lifespan of a solar battery refers to the number of charge-discharge cycles it can undergo before its capacity reduces significantly.
The lifespan of the battery is usually measured in three ways, which are as follows:
- Estimated lifespan in years
- Estimated cycles of the battery
- Estimated throughput
Most manufacturers provide a warranty that guarantees a certain number of cycles or years of service. Choose a solar battery backup for home with a lifespan of up to 7,000 cycles or 5-7 years. Or you should choose batteries that offer a warranty to operate at least 65-70% of their overall capacity.
It’s essential to compare both the lifespan and the terms of the warranty when making a choice.
4- Round-Trip Efficiency:
This metric indicates the amount of energy that can be used as a percentage of the amount of energy that it took to store it.
For instance, if you store 10 kWh of electricity and retrieve 9 kWh, the round-trip efficiency is 90%.
Higher efficiency means more economic value from the stored energy. So, It is recommended to choose a battery for renewable energy storage with an 80% or more efficiency rating; it will help you in the long run.
5- Installation & Maintenance Costs:
Beyond the initial purchase price, it’s vital to consider installation costs, potential maintenance, and the possibility of replacing parts over the battery’s life. Some batteries may appear cost-effective initially but might require more maintenance or replacements.
6- Compatibility with Solar Systems:
Not all batteries integrate seamlessly with all solar setups. Ensure that the battery you’re considering is compatible with your existing or planned solar installation.
7- Safety Features:
Modern solar batteries often come equipped with safety mechanisms like overcharge protection, temperature monitoring, and emergency shutdowns. These features are crucial to prevent potential hazards.
What Are The Benefits Of A Solar System With A Battery Backup?
- Energy Independence: Battery backups provide a degree of energy independence from the grid. During power outages or peak usage times when electricity costs can be higher, a battery system can ensure you still have access to power.
- Maximized Solar Investment: Solar panels often generate excess energy, especially during peak sun hours. With a battery, this excess energy is stored rather than sent back to the grid, ensuring you utilize more of the power you produce.
- Reduced Electricity Bills:By drawing power from your battery during peak rate times or when demand is high, you can avoid or reduce purchasing electricity from the grid at premium prices, thereby saving on energy costs.
- Enhanced Grid Stability:By relying on stored solar energy during peak hours, you contribute to reducing the overall demand on the grid, promoting more stable and efficient grid operations.
- Emergency Power Supply:In cases of natural disasters or blackouts, having a solar system with battery backup can be a lifeline. You’ll have a continued power source when others might be left in the dark.
The Difference Between Grid-Tie vs Off-Grid
When considering solar batteries for your home, one of the foundational decisions you’ll make is whether to have a grid-tie system or go entirely off-grid. Both options come with their own set of benefits and considerations. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
Grid-Tie System (Grid-Connected):

A grid-tie solar system is connected to the local electric grid. Any excess power produced by your solar panels can be fed back to the grid, and similarly, if your panels don’t produce enough energy (like during nighttime), you can draw power from the grid.
Benefits:
- Net Metering:Many regions offer net metering where homeowners can receive credits or compensation for the excess power they feed back into the grid.
- No Need for Large Battery Storage: Since you’re still connected to the grid, you don’t necessarily need a large battery system to cover periods without sun. Some homeowners still choose to have a small battery backup for outages.
- Lower Initial Investment:Without the need for significant storage solutions, the initial setup cost can be lower.
Considerations:
- In cases of grid failures, your home might be without power unless you have a backup battery.
- If your region has varying rates depending on the time of day, you might pay more during peak times unless you have a battery to offset the costs.
Off-Grid System:

An off-grid energy storage system is entirely independent of the local electric grid. This means all the electricity needs of your home must be met by solar panels and stored in batteries for use during non-producing hours.
Benefits:
- Complete Energy Independence: You’re not reliant on the grid or utility companies for power, giving you full control over your energy sources.
- Ideal for Remote Locations: For homes located in areas where connecting to the grid is challenging or costly, off-grid systems are often more practical.
- No Electricity Bills: Without any dependence on utility providers, there are no monthly electricity bills to worry about.
Considerations:
- To ensure uninterrupted power, you’ll need a robust solar panel system and a significant battery storage capacity, which can be costly.
- Being entirely responsible for your power means regular checks and maintenance of the panels, batteries, and other system components.
- Since there’s no grid to fall back on during prolonged cloudy days or during higher-than-usual energy consumption, homeowners need to be more mindful of their energy usage.
FAQs
How to choose solar with a backup battery?
To choose a solar system with battery backup you need to assess your daily energy consumption, consider potential outages, and select a battery with sufficient capacity. Also, ensure system compatibility and opt for high DoD batteries.
What type of battery is best for a home solar system?
Lithium-ion batteries are popular due to their efficiency, lifespan, and decreasing costs. However, the best choice depends on budget, usage patterns, and personal preferences.
How do I know what battery I need for my solar system?
Calculate your home’s daily energy use, consider your desired backup hours, and choose a battery with matching capacity. Ensure it’s compatible with your solar setup.
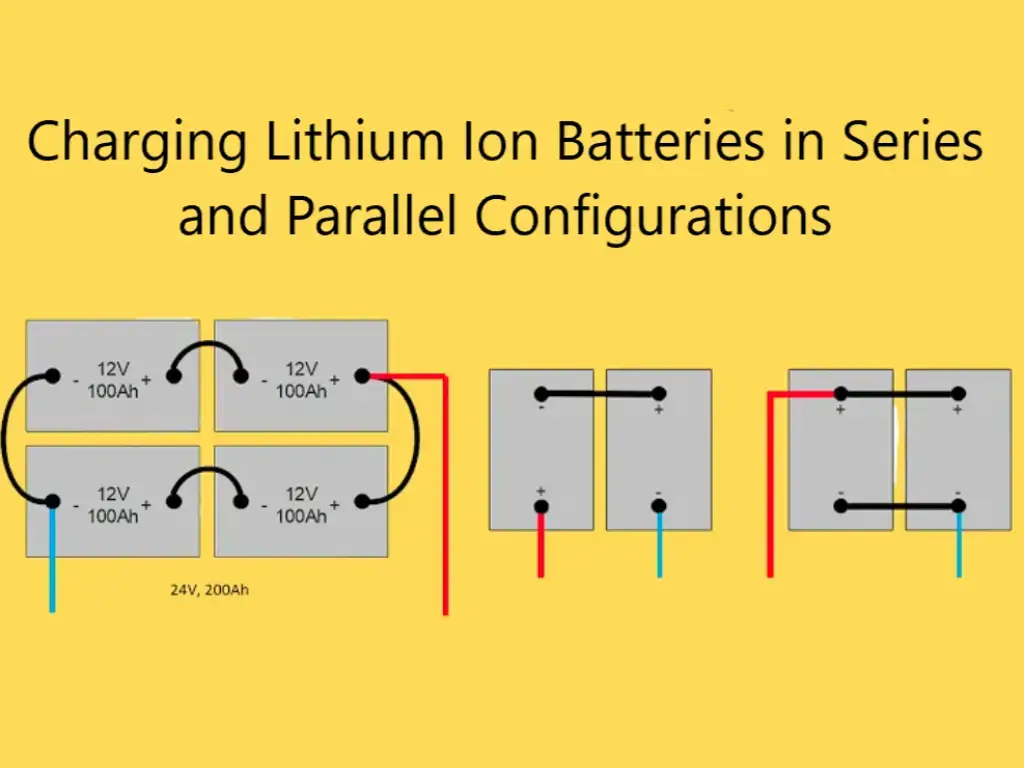
Which is better 12V, 24V, or 48V solar system?
48V systems are generally more efficient, reduce energy loss, and require fewer cables. However, the right voltage often depends on system size and application.
Is series or parallel better for solar panels?
Series connections increase the voltage while keeping the current constant. Parallel increases current with constant voltage. The best configuration depends on system requirements and specific installation conditions.
The Takeaway
Navigating the world of solar batteries can initially seem overwhelming, given the array of options and technicalities. However, with the right knowledge, as provided in this guide, homeowners can make informed decisions that align with their energy needs, budget, and sustainability goals. Investing in a solar battery amplifies the benefits of solar power, bringing enhanced independence, economic advantages, and a reduced carbon footprint. As the sun sets on conventional energy sources, let your home be illuminated by the smart, sustainable choice of solar energy, backed by the perfect battery storage system.